Yes, the account receivable is a sub ledger account. It is an account that is used to record the payment history of each and every customer to whom the business has sold goods or provided services on credit. Accounts receivable represent the amount that the customers owe to the business with respectRead more
Yes, the account receivable is a sub ledger account. It is an account that is used to record the payment history of each and every customer to whom the business has sold goods or provided services on credit.
Accounts receivable represent the amount that the customers owe to the business with respect to the goods sold or services provided to them on credit. They are also known as trade receivable or debtors.
The accounts receivable subledger shows various details of every transaction like the invoice number, amount due, date of payment, discount allowed etc. The subledger accounts are also known as the subsidiary accounts.
Difference between general ledger and subledger accounts
Here is a list of the major differences between sub-ledgers and the general ledger:
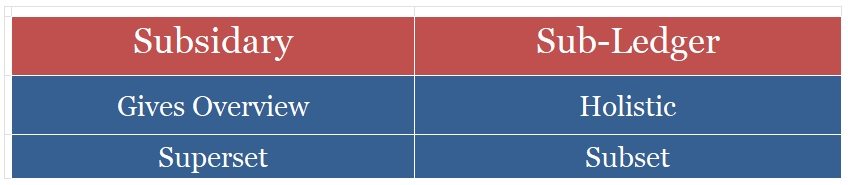
- The subsidiary accounts or the sub ledger are a subset of the general ledger. In other words we can say that subsidiary accounts are a part of the general ledger.
- The trial balance is prepared with the help of the general ledger and not with the help of subsidiary accounts.
- The trial balance is prepared with the help of the general ledger and not with the help of subsidiary accounts.
- The subledger accounts help us to store large volumes of data. They provide us with detailed and comprehensive analysis of each item of financial statements. On the other hand, a general ledger provides us with superficial information about every item in one place.
Importance/ use of Subsidiary Account
The usefulness of an accounts receivable sub ledger account lies in the fact that it provides detailed information about the money different customers owe to the business.
For example, the general ledger account may show that the total balance of trade receivable is 1 lakh without indicating the individual amount that each customer owes to the business. The subsidiary account can help us by showing that customer A owes 50000 rupees, customer B owes 30000 rupees while customer C owes 20000 rupees.
In short, the subsidiary accounts provide detailed information about each and every transaction. They help us to find useful information quickly and easily. They help us analyze the business policies and take corrective actions.
Thus, we can conclude that accounts receivable is a subledger account that provides us detailed information about the various credit transactions and the amount that each customer owes to the business. It helps us analyze our credit policies and take corrective actions. It helps us identify and classify bad debts as such on
See less

Yes, accounting is necessary even for not-for-profit organizations. NPOs or not-for-profit organizations are those that are created for the welfare of the society. They intend to advance some social cause. For example charities, orphanages etc Accounting for NPOs becomes necessary as the trustees ofRead more
Yes, accounting is necessary even for not-for-profit organizations.
NPOs or not-for-profit organizations are those that are created for the welfare of the society. They intend to advance some social cause. For example charities, orphanages etc
Accounting for NPOs becomes necessary as the trustees of these institutions are liable to their members, the donors and the government. They discharge this function with documenting activities of the institution.
What is a not-for-profit organization?
A not-for-profit organization is an entity that undertakes charitable activities. These institutions do not have earning profit as their primary motive. Their focus is on extending social welfare.
Every not-for-profit organization usually has a group of trustees that are responsible for handling all its operations. These trustees are accountable to the members of the NPO.
A not-for-profit organization usually relies on donations and grants as its primary source of revenue. They do not charge the stakeholders to whom they extend their services or goods.
What does accounting for Not-for-profit organizations entail
The professionals undertaking accounting of not-for-profit organizations must have a significant knowledge of statutory provisions and accounting principles. Here is a brief overview of what accounting for a not-for-profit organizations entails
We can conclude that accounting is an indispensable requirements for not-for-profit organizations to be able to continue their operations and claim the statutory benefits that the government has extended to them.
See less