A. Furniture B. Capital C. Sales D. Commission earned
Definition Debit balance may arise due to timing differences in which case income will be accrued at the year's end to offset the debit. The amount is shown in the record of a company s finances, by which its total debits are greater than its total credits. The account which has debit balances are aRead more
Definition
Debit balance may arise due to timing differences in which case income will be accrued at the year’s end to offset the debit.
The amount is shown in the record of a company s finances, by which its total debits are greater than its total credits.
The account which has debit balances are as follows:
• Assets accounts
Land, furniture, building machinery, etc
• Expenses accounts
Salary, rent, insurance, etc
• Losses
Bad debts, loss by fire, etc
• Drawings
Personal drawings of cash or assets
• Cash and bank balances
Balances of these accounts
In class 11th, we learned about all these accounts that have debit balances.
Where the total of the debit side is more than the credit side therefore the difference is the debit balance and is placed credit side as “ by balance c/d “
Here are some examples showing the debit balances of the accounts :
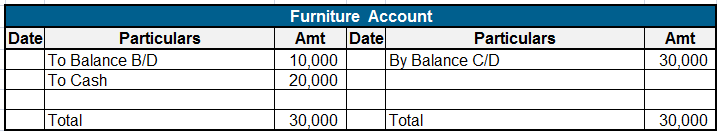
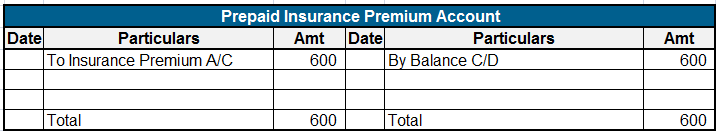
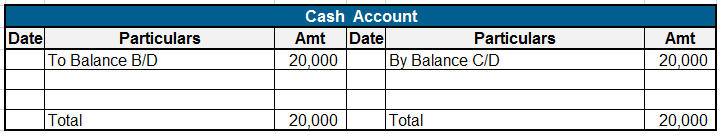

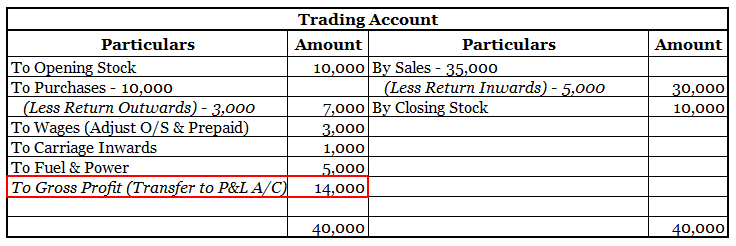
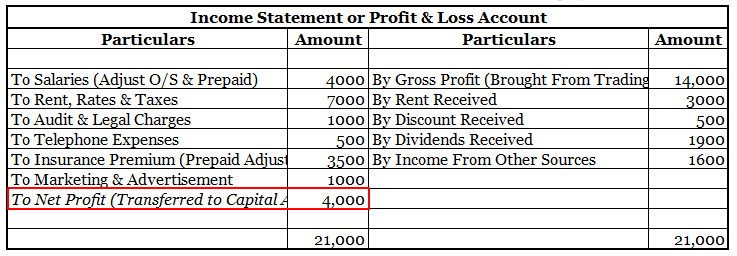
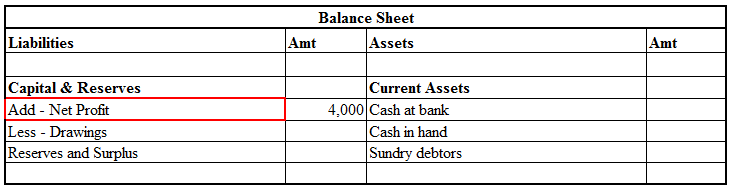
Definition Where the total of the debit side is more than the credit side therefore the difference is the debit balance and is placed credit side as “ by balance c/d “ A furniture account that is an asset has a debit balance. Debit balance may arise due to timing differences in which case income wilRead more
Definition
Where the total of the debit side is more than the credit side therefore the difference is the debit balance and is placed credit side as “ by balance c/d “
A furniture account that is an asset has a debit balance.
Debit balance may arise due to timing differences in which case income will be accrued at the year’s end to offset the debit.
The amount is shown in the record of a company s finances, by which its total debits are greater than its total credits.
The account which has debit balances are as follows:
Land, furniture, building machinery, etc
Salary, rent, insurance, etc
Bad debts, loss by fire, etc
Personal drawings of cash or assets
Balances of these accounts
The account has credit balances as follows:
Creditors, bills payable, etc
Salary received, interest received, etc
Dividends, interest, etc
Partners Capital
Here are some examples showing the debit balances and credit balances of the accounts :

See less