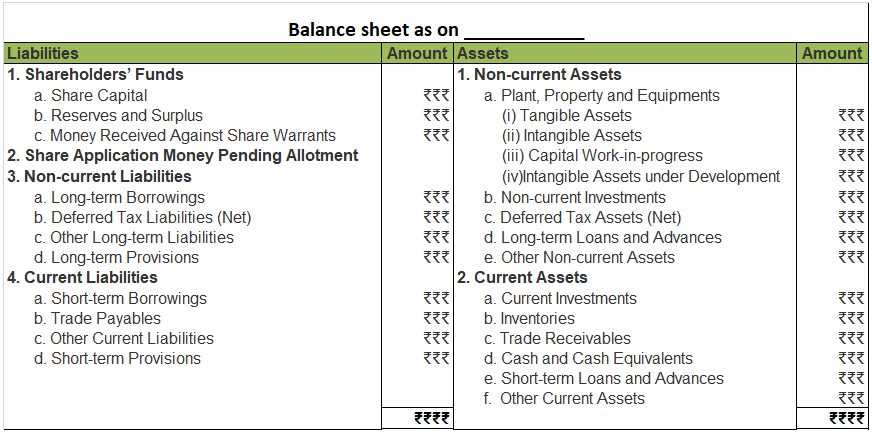
A balance sheet of a company is a financial statement that depicts the assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity of the company at a point of time, usually at the end of the accounting year. A balance sheet of a company is reported in a vertical format which is different from that of a partnershiRead more
A balance sheet of a company is a financial statement that depicts the assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity of the company at a point of time, usually at the end of the accounting year. A balance sheet of a company is reported in a vertical format which is different from that of a partnership where the horizontal format is used.
COMPONENTS OF A BALANCE SHEET
The three main components of a balance sheet are Assets, Liabilities and Shareholders’ equity.
- Assets: They are divided into two main categories that are current assets and non-current assets. If an asset is expected to be realised within 12 months or is primarily held for being traded, or is cash or cash equivalent, then those assets are termed as current assets. All assets that are not current assets are grouped under non-current assets. They are normally realised after 12 months.
- Liabilities: They are categorised as current liabilities and non-current liabilities. If the amount owed by the company to an outside party is due to be settled in 12 months, then it can be termed as a current liability. The rest of the liabilities are referred to as non-current liability.
- Shareholders’ Equity: This is the money owed to the owners of the company, that is shareholders. It is also called net assets since it is equal to the difference between total assets and total liabilities. Their main categories are Shareholders’ Capital and Reserves and Surplus.
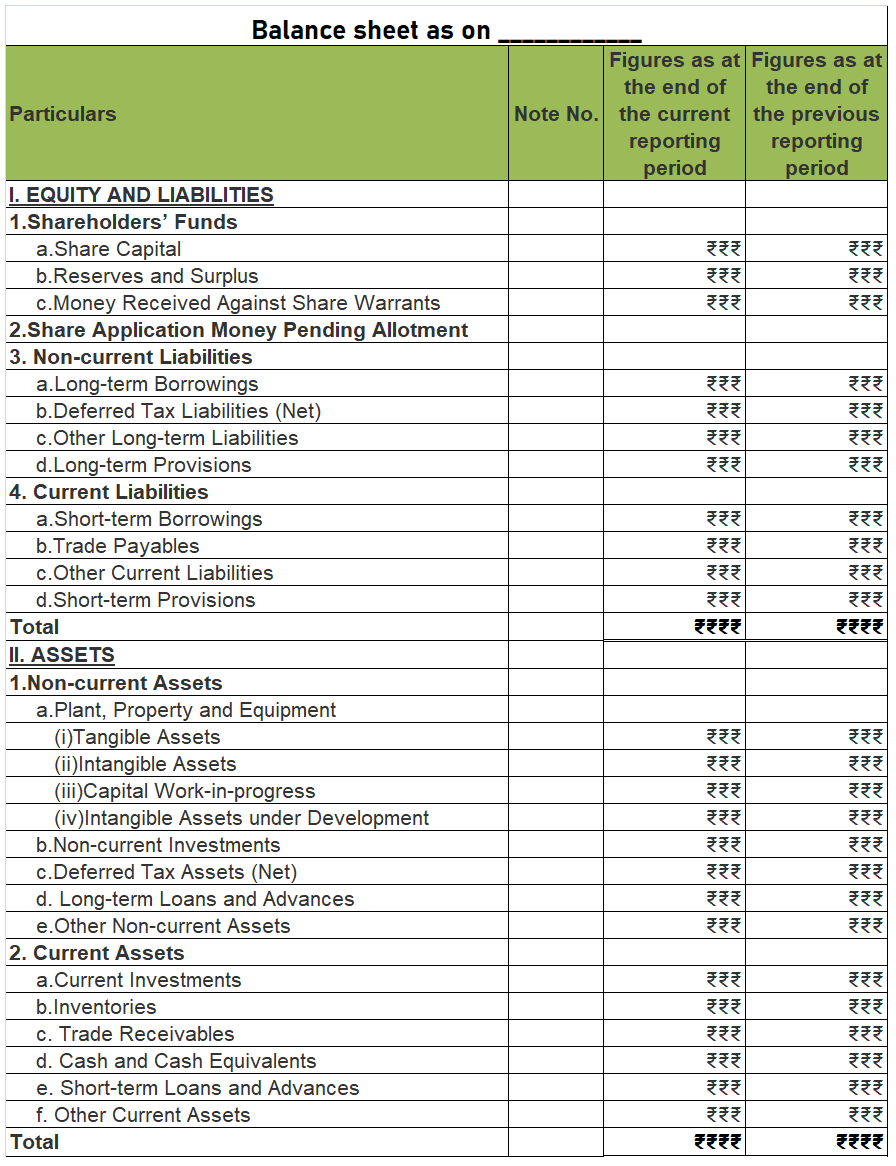
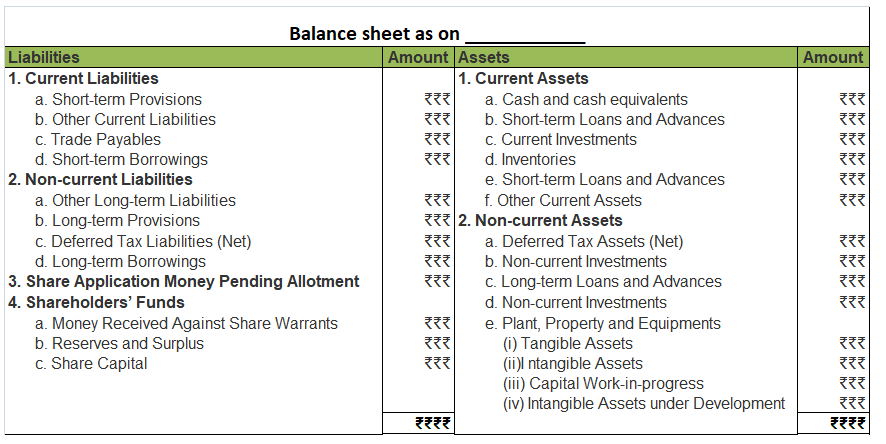
FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
As per the Companies Act 2013, the following format should be used for preparing a balance sheet.

From the above Balance sheet, we should get:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity
Relevant notes for each component should also be prepared when necessary.
See less
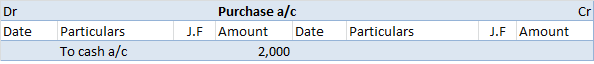
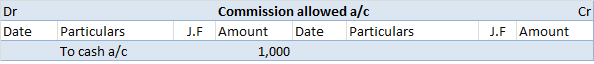
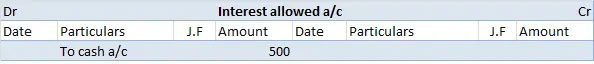
Introduction A capital reduction account is an account used to pass entries related to the internal reconstruction of a company. During reconstruction, paid-up capital reduced is credited to this account; hence its name is capital reduction account. It is also known as the reconstruction account. TyRead more
Introduction
A capital reduction account is an account used to pass entries related to the internal reconstruction of a company. During reconstruction, paid-up capital reduced is credited to this account; hence its name is capital reduction account. It is also known as the reconstruction account.
Type of account
A capital reduction account is a temporary account open just to carry out internal reconstruction. It represents the sacrifices made by the shareholders, debenture holders and creditors. Also, any appreciation in the value of assets is credited to this account. It is closed to capital reduction when internal reconstruction is completed.
Entries passed through capital reduction account
When paid-up capital is cancelled.
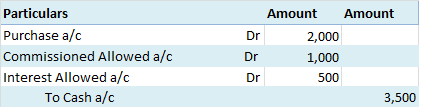
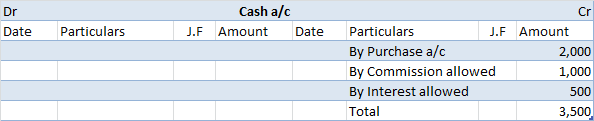
When paid-up capital is cancelled, the share capital account is debited and the capital reduction account is debited as share capital is getting reduced.
When assets and liabilities are revalued
At the time of internal reconstruction, the gain or loss on revaluation is transferred to the capital reduction account instead of the revaluation reserve.
Writing off of accumulated losses and intangible assets
The credit balance of the capital reduction account is used to write off the accumulated losses and intangible assets like goodwill, patents etc which are unrepresented by capital. The capital reduction account is debited and profit and loss account and intangible assets accounts are credited.
Treatment in books of account
The balance in the capital reduction account, whether debit or credit, it is transferred to the capital reduction account. Hence, it doesn’t appear on the balance sheet.
See less