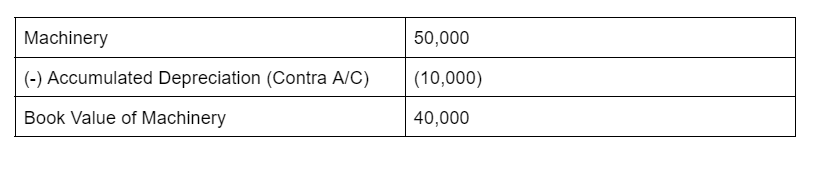
The debts that have a higher chance of not being paid are called doubtful debts. They are a part of the regular dealing of the company and may arise due to disputes or treachery on the part of debtors. Bad debts refer to the doubtful debts that no longer seem to be recoverable from the business. WriRead more
The debts that have a higher chance of not being paid are called doubtful debts. They are a part of the regular dealing of the company and may arise due to disputes or treachery on the part of debtors.
Bad debts refer to the doubtful debts that no longer seem to be recoverable from the business.
Written off means an expense, income, asset, liability is no more recorded in the books of accounts because they no longer hold relevance for the business.
When doubtful debts turn into bad debt, they are written off from the books after a stipulated time as they no longer seem recoverable.
If any cash is received against such bad debts that were written off, it is known as cash received against bad debts written off. Cash is received against bad debts usually when the debtor is declared insolvent and money is recovered from its estate.
Bad debts recovered are considered an income for the company as they were previously written off as a loss and any cash received against it is considered as income.
Journal entry for such situation is:
Cash or Bank A/c (Dr.)
To Bad Debts Recovered A/c
We debit the increase in assets, and since cash is coming into the business it is debited.
We credit the income, and since bad debts recovered is an income to the business it is credited.
See less

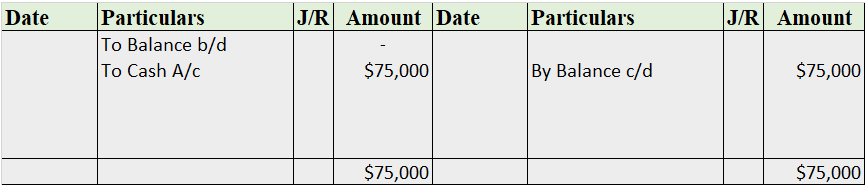
Under GST, Input Tax Credit (ITC) refers to the tax already paid by a person on input, which is available as a deduction from tax payable on output. This means that if you have paid tax on some purchases, then at the time of paying tax on the sale of goods, you can reduce it by the amount you alreadRead more
Under GST, Input Tax Credit (ITC) refers to the tax already paid by a person on input, which is available as a deduction from tax payable on output. This means that if you have paid tax on some purchases, then at the time of paying tax on the sale of goods, you can reduce it by the amount you already paid on purchase and pay only the balance amount.
EXAMPLE
Suppose Ashok purchased goods worth Rs 100 while paying tax at 10%, that is Rs 10. He now sold the goods for Rs 200, with a tax payable of Rs 20. Now, Ashok can avail input tax credit of Rs 10 that he already paid for the purchase and hence the net tax payable is Rs 10 (20-10).
METHOD OF UTILISATION OF ITC
The central government collects CGST, SGST, UTGST or IGST based on whether the transactions are done intrastate or interstate.
The amount of input tax credit on IGST is first used for paying IGST and then utilised for the payment of CGST and SGST or UTGST. Similarly, the amount of ITC relating to CGST is first utilised for payment of CGST and then for the payment of IGST. It is not used for the payment of SGST or UTGST. Meanwhile, the amount of ITC relating to SGST is utilised for payment of SGST or UTGST and then for the payment of IGST. Such amounts are not used for payment of CGST.
We can see how Input Tax Credit is used from the below example and table:

See less