Personal Accounts: The accounts of persons, firms, companies, etc. are personal accounts. There is a further classification to personal accounts- Accounts of Natural Persons: The transactions relating to individual human beings fall under this category. For Example, accounts of Joseph, Richard, MorrRead more
Personal Accounts: The accounts of persons, firms, companies, etc. are personal accounts. There is a further classification to personal accounts-
- Accounts of Natural Persons: The transactions relating to individual human beings fall under this category. For Example, accounts of Joseph, Richard, Morris, etc.
- Accounts of Artificial Persons: The transactions relating to firms, organizations, companies, institutions, associations, etc. fall under this category. For Example, Oil India Ltd, Symbiosis college, Assam Tea company, etc.
- Representative Personal Accounts: The transactions relating to certain person or a group of persons, although the name of the concerned person or persons are not mentioned in the account head, such types of accounts come under this head. Such type of accounts generally include outstanding accounts or prepaid accounts. For Example, accounts like wages outstanding, outstanding salary, commission received in advance, salary prepaid, etc.
Note: When any Prefix or Suffix is used before/ after any nominal account head, such account is classified as Representative personal account under traditional approach.
For Example, Salary A/c is a nominal account whereas salary outstanding A/c is a personal account as the word outstanding is being used as a prefix to Salary A/c.
The Accounting rule for Personal Account is –
Debit the Receiver of the benefit.
Credit the Giver of the benefit.
Real Account: The transactions relating to tangible things i.e. the things that can be seen, touched and physically exchanged and the intangible things that cannot be seen, touched but the presence can be felt comes under this category. For Example, tangible things like Cash, goods, building, machinery, etc. and intangible things like goodwill, patent, trademarks, etc.
The Accounting rule for Real Account is –
Debit what comes in.
Credit what goes out.
Nominal Accounts: The transactions relating to losses, expenses, incomes and gains comes under this category. For Example, Rent paid, wages paid, commission received, interest paid/ received, etc.
The Accounting rule for Nominal Account is –
Debit Expenses and Losses.
Credit Gains and Incomes.
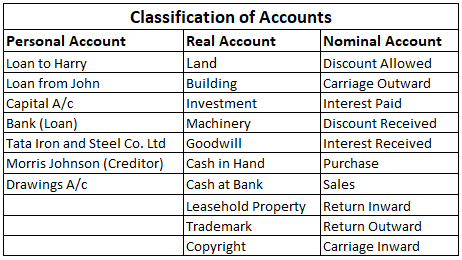
Some Common Examples under the three heads are

Cash Book is called a journalized ledger because it is considered to be both a journal as well as a ledger. As you know Cash Book is a subsidiary book. But like a journal, the transactions in the Cash Book are recorded in it for the first time from the source documents/vouchers. Hence it is considerRead more
Cash Book is called a journalized ledger because it is considered to be both a journal as well as a ledger.
As you know Cash Book is a subsidiary book. But like a journal, the transactions in the Cash Book are recorded in it for the first time from the source documents/vouchers. Hence it is considered to be a journal for all cash transactions.
Cash Book can also be viewed as a Cash A/c because all transactions involving cash are recorded in it. It provides a summary of cash transactions. Hence it is considered to be a ledger account for cash transactions.
Since Cash Book is both a journal and ledger, you can very well call it a ‘journalized ledger’.
See less