Introduction Furniture is treated as a fixed asset of an enterprise unless it deals in the manufacturing or the trade of furniture. As stock in trade, it will be treated as current assets. In both cases, they are real accounts. Hence, the golden rule of accounting will be the same. But, when it coRead more
Introduction
Furniture is treated as a fixed asset of an enterprise unless it deals in the manufacturing or the trade of furniture. As stock in trade, it will be treated as current assets.
In both cases, they are real accounts. Hence, the golden rule of accounting will be the same.
But, when it comes to journal entries, Furniture A/c will appear only when it is treated as a fixed asset.
No journal entries are passed in the stock-in-trade account except for some balance transferring entries.
Journal Entries on taking Furniture as a fixed asset
Taking furniture as a fixed asset, we can pass various entries related to it. Since furniture is an asset, any increase is debited and the decrease is credited.
Also, furniture is a real account which means the golden rule of accounting applicable is, “Debit what comes in and credit what goes out”.
Following are the basic entries related to furniture.
Purchase of furniture
The most common entry related to furniture is the purchase of furniture:
| Furniture A/c Dr. | Amt | |
| To Cash / Bank A/c | Amt |
Here Furniture A/c is increased, hence debited.
Cash or Bank being reduced is credited.
Sale of furniture
| Cash / Bank A/c Dr. | Amt | |
| Profit and Loss A/c * Dr. | Amt | |
| To Furniture A/c | Amt | |
| To Profit and Loss A/c ** | Amt |
*In case of loss
**In case of profit
On the sale of furniture, its balance gets reduced, hence credited.
Cash or Bank is debited as cash comes in hand or into the bank.
Also, profit or loss may arise due to the difference in sale value and the carrying amount of the furniture A/c.
The difference is debited to Profit and Loss A/c in case of loss and credited in case of profit.
Depreciation on Furniture
| Depreciation A/c Dr. | Amt | |
| To Furniture A/c | Amt |
Here, furniture is credited as it is decreased by the amount of depreciation.
Depreciation being a non-cash expense, is debited.
Journal Entries on taking Furniture as stock in trade
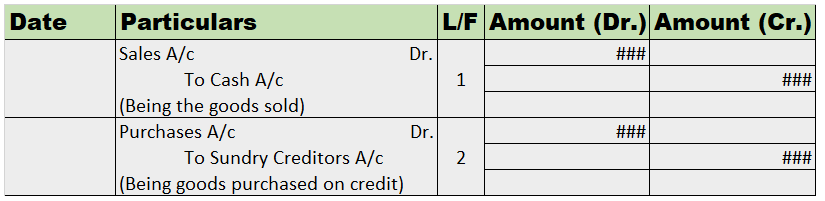
When furniture is stock of trade of a business, the journal entries will be like normal purchase and sales entries as below:
| Purchase A/c Dr. | Amt | |
| To Cash / Bank A/c | Amt |
| Cash / Bank A/c Dr. | Amt | |
| To Sales A/c | Amt |
There will be no furniture account.
See less
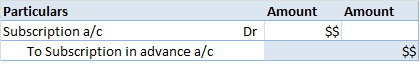
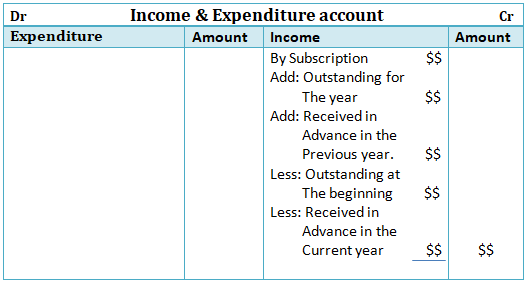
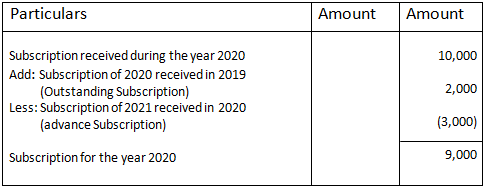
Meaning We know that an account in ledger format has two amount columns i.e. debit and credit amount columns. Now, most of the time, the total of debit and credit sides do not match. The difference between their totals is called the balance of the account and it is posted on the shorter side. ThisRead more
Meaning
We know that an account in ledger format has two amount columns i.e. debit and credit amount columns. Now, most of the time, the total of debit and credit sides do not match. The difference between their totals is called the balance of the account and it is posted on the shorter side. This result in equalling the total of both sides, hence this act is called ‘balancing an account.
Types of balances
Balancing an account is a very usual practice so that the balance of an account can be known. An account can have two types of balances:
The balance of an account is posted on the shorter side. It means:
Example
The following is a cash account that is not balanced:
We can see the debit side is ₹800 more than the credit side. It means there is a debit balance. It will be posted on the credit side as ‘By balance c/d’ to balance the account.
Exceptions
Balance of the income and the expense accounts (nominal accounts)are not computed. Instead, they are closed to trading account or profit and loss account to balance their amount totals. For example, the salaries account and sales accounts
Only the balance of the following types of accounts are computed and carried forwarded to successive accounting years:
The balance of these accounts is shown on the trial balance and balance sheet as well.
See less