Yes, Goodwill is a fixed asset because it adds to the value of the business over a long period. Goodwill can never be calculated for a short period. GOODWILL Basically, goodwill is a premium or you can say an additional price you are paying because of the reputation of a firm or a person. YouRead more
Yes, Goodwill is a fixed asset because it adds to the value of the business over a long period. Goodwill can never be calculated for a short period.
GOODWILL
Basically, goodwill is a premium or you can say an additional price you are paying because of the reputation of a firm or a person.
You may have seen some famous shop in your locality which usually charges a higher price as compared to the other local shops selling the same product.
You may have also noticed that bigger brands like Bata, Titan, Zara, etc. charge higher prices for their products as compared to the same products available in the local market and people are even willing to pay for them. Ever wondered why?
This is because of the goodwill created by them over the years by providing quality products and services, good employee relationships, a strong customer base, social service, a brand name and so on. Customers trust them and for this trust, they are even willing to pay higher prices.
Goodwill is the quantitative value (i.e. in monetary terms) of the reputation of the firm in the market.
FIXED ASSETS
An asset is any possession or property of the business that enables the firm to get cash or any benefit in the future.
Fixed Assets are assets which are purchased for long-term use. They are for continued use in the business for producing goods or services and are not meant for resale. For example- Plant, machinery, building, goodwill, patents etc.
Fixed assets can be tangible or intangible.
Tangible assets are those assets which can be seen and touched and have physical existence like Plant and machinery, building, stock, furniture etc.
Intangible assets are those assets which cannot be seen or touched i.e. they don’t have any physical existence like goodwill, patent, trademark, prepaid expenses etc. Even though they can’t be seen or touched by they have value and are not fictitious assets.
Goodwill as a Fixed Asset
Goodwill is an intangible asset as it cannot be seen or touched but has value and adds value to the business over a long period. Thus, goodwill is a fixed asset.
It is shown in the balance sheet as a Fixed asset under the head Intangible asset.
Goodwill can be
- Self-generated (Non-Purchased goodwill)
- Purchased goodwill
Self-generated goodwill is created over a period due to the good reputation of the business. It is the difference between the value of the firm and the fair value of the net tangible assets of the firm.
Goodwill = Value of the firm – Fair value of net tangible assets
Here, F.V of net tangible assets = Fair value of tangible assets- Fair value of tangible liabilities
Purchased goodwill arises when one business purchases another business. It is the difference between the price paid for the purchased firm and the sum of the fair market value of the assets received and liabilities to be paid by them on behalf of the purchased firm.
Goodwill = Purchase price – (F.V of assets received + F.V of liabilities to be paid)
Only purchased goodwill is recorded in the books of accounts because it is difficult to correctly calculate the value of self-generated goodwill as the future is uncertain, also its valuation depends on the judgement of the person calculating it, which defers from person to person. Since there is no fixed standard to calculate self-generated goodwill only purchased goodwill is recorded as the price paid for it at the time of acquiring another business.
Suppose Firm A acquired Firm B.
Purchase price= $100,000
Assets received=$60,000
Liabilities (to be paid by Firm A on behalf of Firm B) = $10,000
Goodwill = $100,000 – ($60,000 + $10,000) = $30,000
This, goodwill of $30,000 will be recorded under the head Fixed Asset, subhead Intangible Assets in the balance sheet of Firm A (that is in the balance sheet of the acquiring firm)
See less

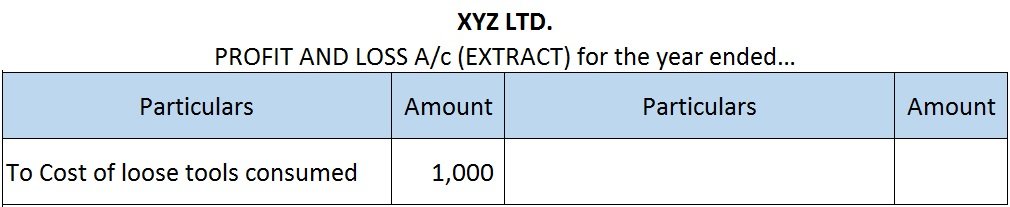
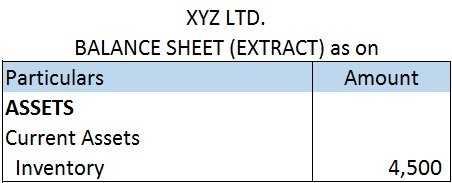
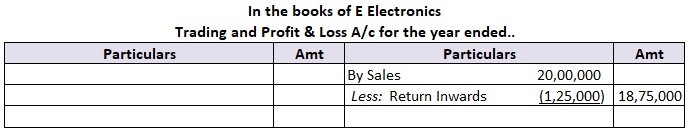
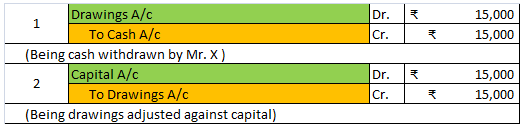
Yes, a creditor is a liability. Creditors are treated as current liability. A creditor is a person who provides money or goods to a business and agrees to receive repayment of the loan or the payment of goods at a later date. The loan may be extended with or without interest. Creditors may be secureRead more
Yes, a creditor is a liability. Creditors are treated as current liability.
A creditor is a person who provides money or goods to a business and agrees to receive repayment of the loan or the payment of goods at a later date. The loan may be extended with or without interest.
Creditors may be secured creditors or unsecured creditors. In the case of secured creditors, some collateral is usually pledged to them. In the case of a default, they can sell or otherwise dispose of the collateral in any manner to recover the money due to them.
In the case of unsecured creditors, no collateral is pledged against the amount due to them. In the case of a default, they can approach a Court to enforce repayment but cannot sell any asset of the company by themselves.
Why are Creditors treated as a liability?
An asset is something from which the business is deriving or is likely to derive economic benefit in the future. The business has legal ownership of that asset which is legally enforceable in a court of law. For example, Plant and Machinery, accrued interest, building, etc
A liability is a legal obligation of the business. It may be in the form of outstanding payments or loans or the owner’s share of the company that the company has to pay them as and when demanded.
As the company has a legal obligation to pay money to the creditor, they are treated as a liability. Most creditors are to be repaid within 1 year and are hence classified as current assets.
Treatment and Importance of Creditors
Creditors are mostly treated as current liabilities. They are shown under the head “current liabilities” of the balance sheet of a company.
The significance/importance of creditors is as follows:
We can conclude that the creditor being a person to whom the business is legally liable to pay a certain sum of money after a certain period of time has to be classified as a liability.
Creditors play a major role in determining the success of a business. They act as a major constituent of the supply cycle of the business and affect the cash flows of the business. They are shown under the head “current liabilities” of the balance sheet of a company.
See less