Let the business in our example be X Trading. The 15 transactions are as follows: 1st April - X Trading started its business with Rs. 10,000 cash and furniture of Rs. 5,000. 5th April - Purchased 1,000 units of goods for Rs. 1,000 in cash from Ram. 10th April – Bought stationery for Rs. 100 in cash.Read more
Let the business in our example be X Trading. The 15 transactions are as follows:
- 1st April – X Trading started its business with Rs. 10,000 cash and furniture of Rs. 5,000.
- 5th April – Purchased 1,000 units of goods for Rs. 1,000 in cash from Ram.
- 10th April – Bought stationery for Rs. 100 in cash.
- 25Th April – Sold 500 goods for Rs. 750 in cash.
- 1st May – Paid a rent of Rs. 1200 ( 1st April to 31st March)
- 1st June – Took a loan of Rs. 15,000 from the bank at interest@10%.
- 15Th June – Sold 400 goods for Rs. 600 to Shyam in credit.
- 1st August – Bought a computer for Rs. 10,000 in from ABC Computers in credit.
- 15th October – Received Rs. 300 from Shyam in cash.
- 1st November – Purchased 2,000 units of goods for 2,000 from Ram in credit.
- 15th November – Paid Rs. 5,000 to ABC Computers through cheque.
- 1st December – Sold 1,000 units of goods for Rs. 1,500. Received cheque as payment.
- 1st January – Obtained Trade license (valid for 5 years) by paying fees of Rs. 1000 through online bank transfer.
- 15Th February – Paid Rs. 1,500 to Ram. Through cheque.
- 15Th March – Drawings made of Rs. 2000 in cash.
We will prepare the journal, ledgers and the trial balance from the above transactions.
Journal
Journal is known as the book of primary entry or book of original entry. It is because every transaction is recorded in form of journal entries in the journal. Every journal entry affects at least two accounts (dual effect). A transaction has to be a monetary transaction otherwise it cannot be recorded as a journal entry.
The procedure of recording transactions as journal entries is simple if we follow the modern rules of accounting.
So first we have to identify which and what type of account does a transaction affect. The types of accounts are:
- Asset – Debit in case of increase Credit in case of decrease.
- Liabilities – Debit in case of decrease Credit in case of increase.
- Capital – Debit in case of decrease Credit in case of increase.
- Expense – Debit in case of increase Credit in case of decrease.
- Income – Debit in case of decrease Credit in case of increase.
Ledger
Ledgers are known as the books of principal entry or book of final entry. All the journal entries recorded in the journal are posted to the ledgers. A Ledger is where the entries related to a particular account are recorded. For example, all the transactions related to salary will be recorded in the salary account ledger.
It is very important to prepare the ledger to arrive at the balance of each account in the books of concern so that it can prepare its trial balance.
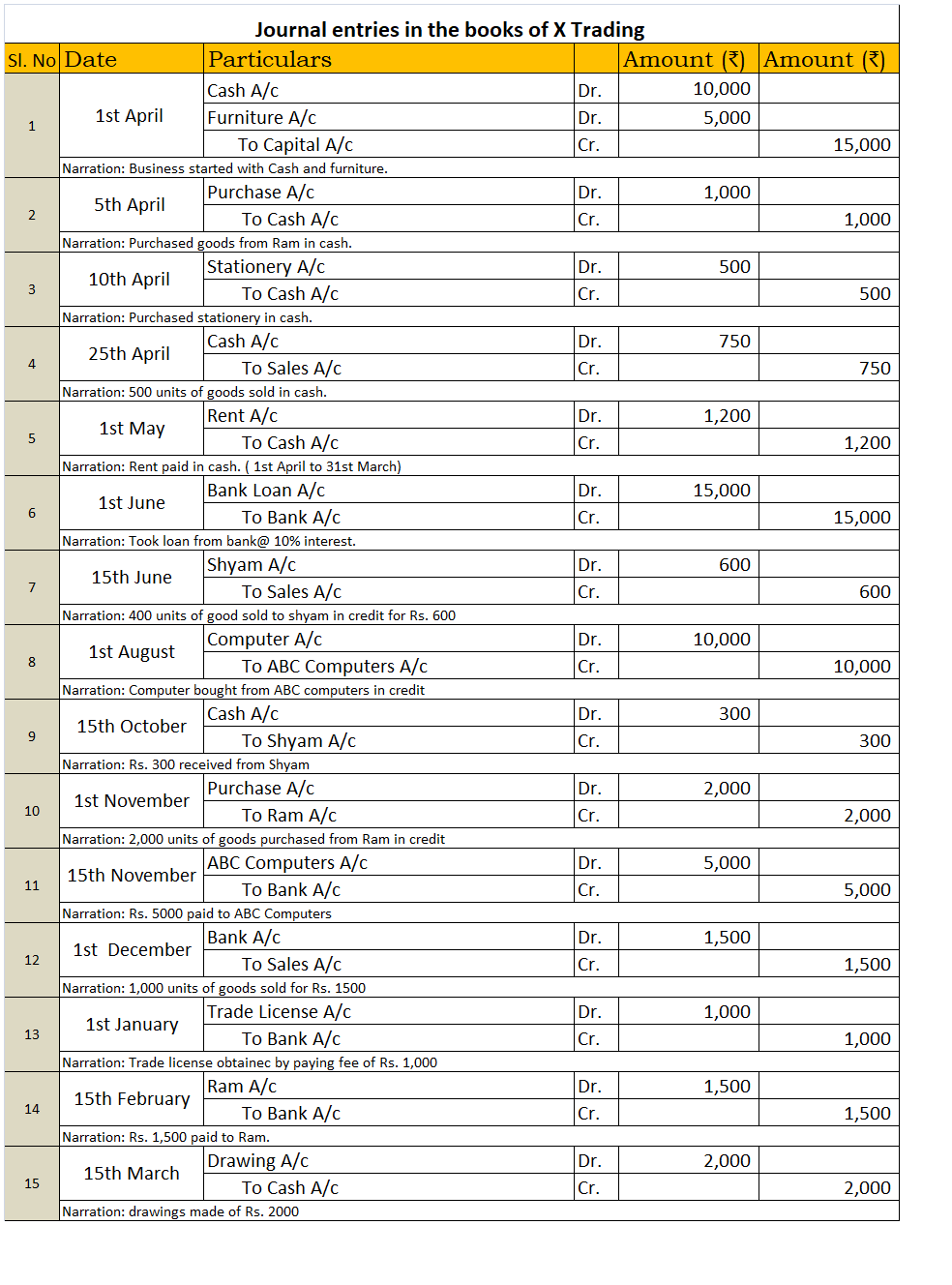
The procedure of posting journal entries in the ledger account is done is as follows:
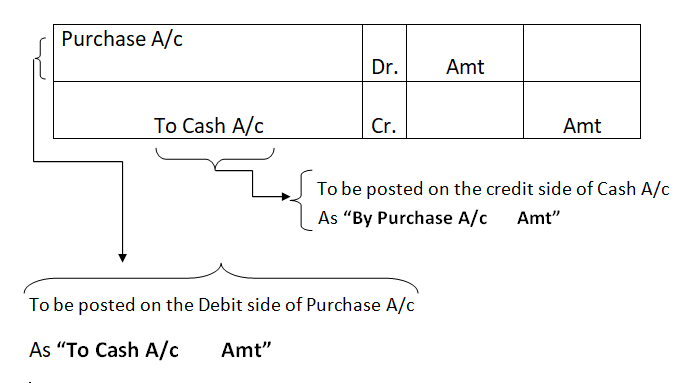
The ledgers are as follows:
Trial Balance
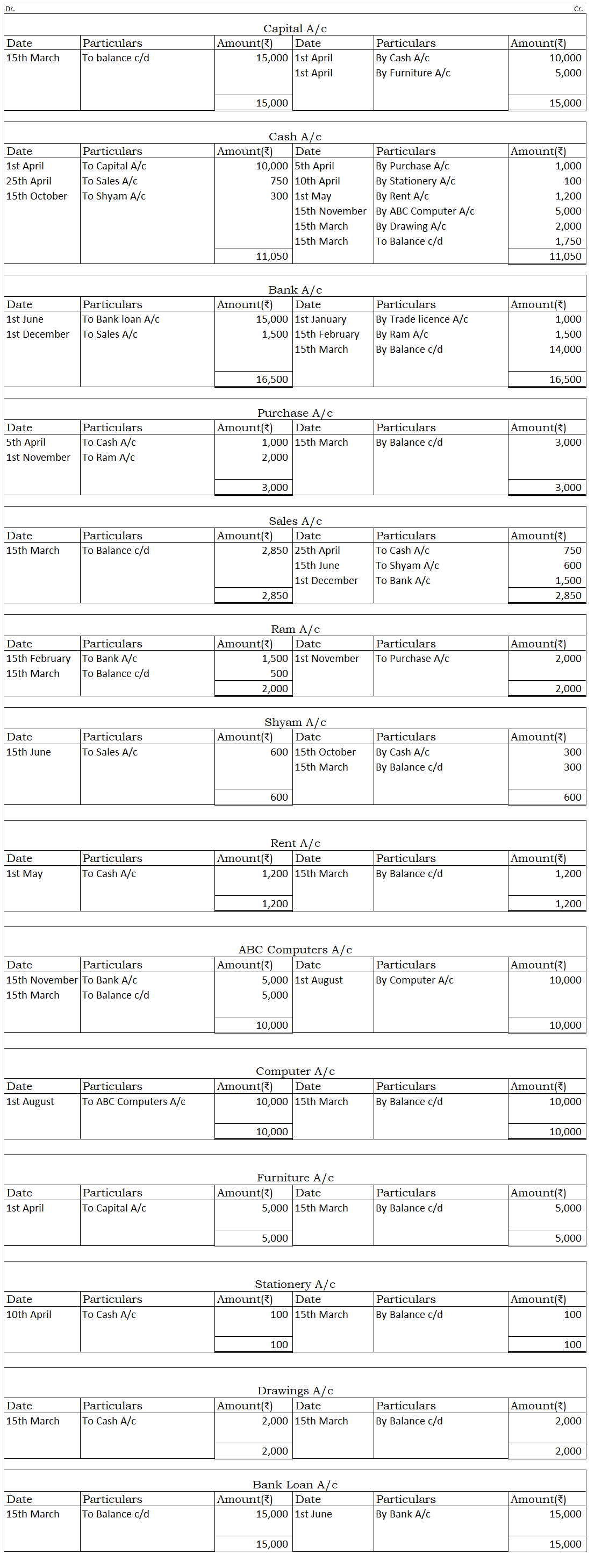
The trial balance is not a part of the books of accounts. It is just a statement prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the books of the accounts. It also helps to know about the omission and posting mistakes. It is prepared after the ledger accounts have been drawn and their balances have been ascertained.
The balance of all the ledger accounts is posted on either side of the trial balance. Debit balance of the account on the debit side and credit balance of the account on the credit side.
Also, the closing stock from the financial statements of the previous year is posted on the debit side of the trial balance as opening stock to account for the stock with the business at the beginning of the financial year.
Following is the trial balance of X trading:

Let’s understand what a cashbook is: A petty cash book is a cash book maintained to record petty expenses. By petty expenses, we mean small or minute expenses for which the payment is made in coins or a few notes like tea or coffee expense, bus or taxi fare, stationery expense etc. Such expenses areRead more
Let’s understand what a cashbook is:
The manner in which entries are made
When cash is given to the petty cashier, entry is made on the debit side and in the petty cashbook and credit entry in the general cashbook.
Entries for all the expenses are made on the credit side.
Generally, the petty cashbook is prepared as per the Imprest system. As per the Imprest system, the petty expenses for a period (month or week) are estimated and a fixed amount is given to the petty cashier to spend for that period.
At the end of the period, the petty cashier sends the details to the chief cashier and he is reimbursed the amount spent. In this way, the debit balance of the petty cashbook always remains the same.
Format and items which appear in the petty cashbook
The format of the petty cashbook depends upon the type of petty cash book is prepared and the items appearing in it are nothing but petty expenses. Let’s see an example:-
A business incurred the following petty expenses for the month of April:-
Now we will prepare two types of cashbooks:
Here, the Petty cash book is of the same format as the general cash book.
The cash allocated for petty expenses is recorded on the debit side of the petty cash book and on the credit side of the general cash book.
Here, there are separate amount columns for each type of expense. As the name suggests, this type of petty cashbook helps to analyse the petty cash spending on basis of the type of expense.
See less