Brief Introduction The stock of finished goods left unsold at the end of the year is known as closing stock. As closing stock represent an asset i.e. the unsold finished goods, it has a debit balance. Closing stock appears on the credit side of the trading account and on the asset side of the balanRead more
Brief Introduction
The stock of finished goods left unsold at the end of the year is known as closing stock. As closing stock represent an asset i.e. the unsold finished goods, it has a debit balance.
Closing stock appears on the credit side of the trading account and on the asset side of the balance sheet. But, if closing stock is adjusted against purchase i.e. deducted from purchase account balance, then it doesn’t appear in the trading account.
It is always shown on the asset of the balance irrespective of its treatment as discussed above because it is an asset.
Though no ledger is maintained for closing stock in financial accounts of a business, the journal entry for the closing stock is passed and is as below:
Closing stock A/c Dr Amt
To Trading A/c Amt
(When the closing stock appears in trading a/c)
OR
Closing stock A/c Dr Amt
To Purchase A/c Amt
(When closing stock is adjusted against purchase A/c and not shown in trading a/c)
Generally, the closing stock is shown separately in the trial balance because it is already part of the purchase account balance.
Closing stock is ascertained at the end of the financial year and it has great importance as it directly affects the gross profit or loss of a business. Closing stock at end of a year becomes the opening stock of the next financial year.
Numerical Example
ABC trading reported the following particulars at the end of the financial year 20X2-20X3:
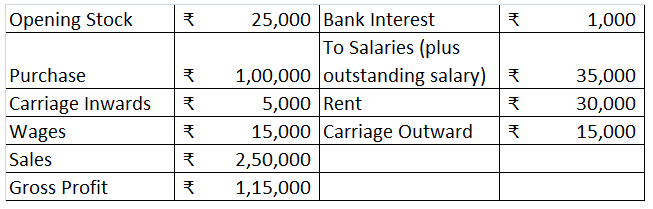
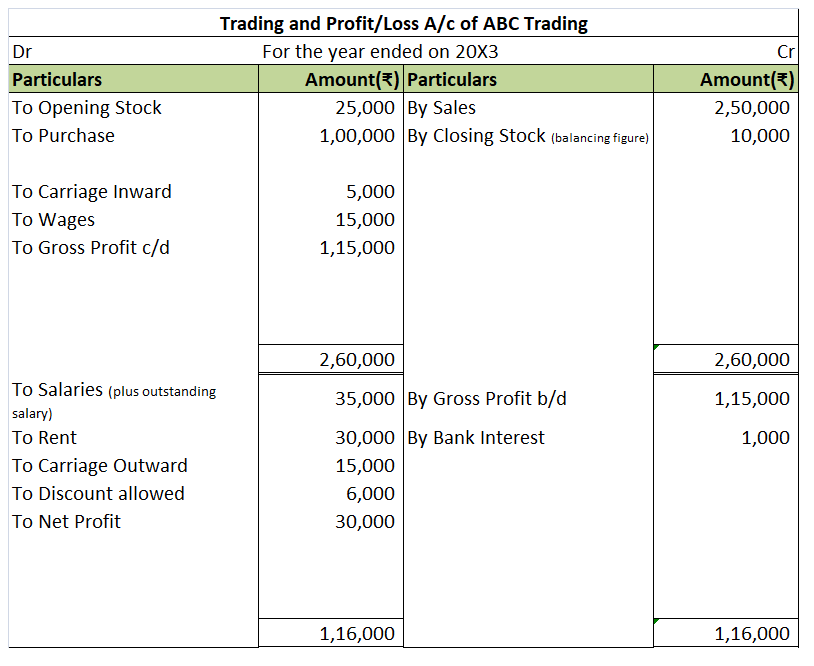
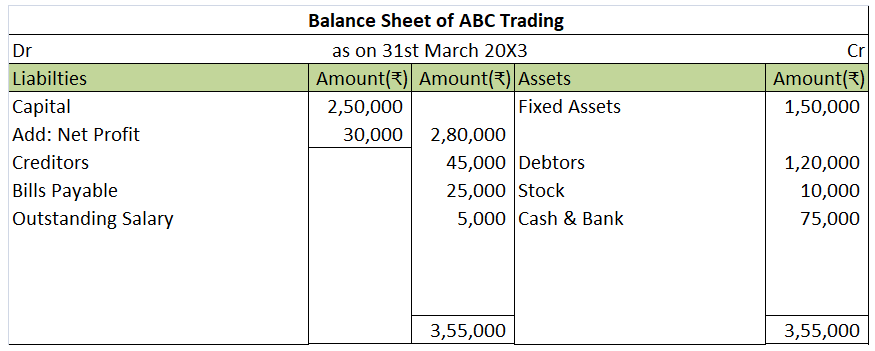
We will draw the trading and P/L account and balance sheet of ABC Trading using the above information.
As the closing stock is not given, we will calculate the closing stock as a balancing figure.
It can be also calculated using this formula:
Closing stock = Opening stock + Purchase + Gross Profit – Sales

The principal book of accounting is “Ledger”. It records all types of transactions relating to a real, personal or nominal account. It records transactions relating to an income, expense, asset or a liability. A ledger classifies a transaction which is recorded in journal to their respective accountRead more
The principal book of accounting is “Ledger”. It records all types of transactions relating to a real, personal or nominal account. It records transactions relating to an income, expense, asset or a liability.
A ledger classifies a transaction which is recorded in journal to their respective accounts, and in the end calculates a closing balance for the same account. The closing balance is further transferred to the financial statements, and hence ledger is called the books of final entry as it gives true and fair picture of an account.
Template of Ledger:
For example, ABC Ltd purchased machinery for cash amounting to Rs 1,00,000 on 1st January. This transaction will include a machinery account and a cash account. The amount will be recorded in the respective accounts for that period.
The reason being ledger is called a principal book of accounting is, it helps a business in preparation of trial balance and financial statements.
See less