The correct option is Option C: Journal Entries. Journal entries are the primary entries in the books of accounts and they are passed when any transaction or event takes place. Every journal entry has a dual effect i.e. two or more accounts are affected. For example, When cash is introduced in the bRead more
The correct option is Option C: Journal Entries.
Journal entries are the primary entries in the books of accounts and they are passed when any transaction or event takes place. Every journal entry has a dual effect i.e. two or more accounts are affected.
For example, When cash is introduced in the business, the journal entry passed is:
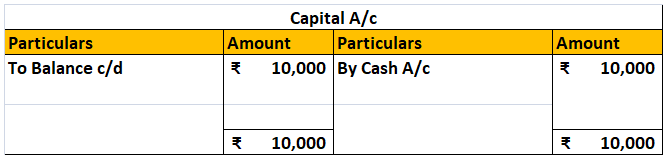
Cash A/c Dr. ₹10,000
To Capital A/c ₹10,000
The accounts affected here are Cash A/c and Capital A/c.
Cash A/c gets debited by ₹10,000,
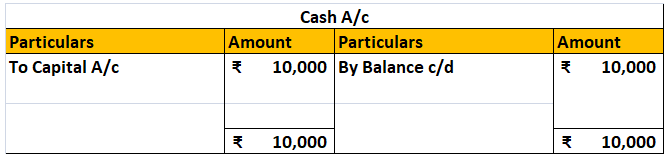
and Capital A/c get credited by ₹10,000.
All the processes of accounting are conducted in an ordered manner known as the accounting cycle.
The first step in an accounting cycle is to identify the transactions and events which are monetary in nature.
The second step is to record the identified transactions in form of journal entries.
And the third step is to make postings in the general ledger accounts as per the journal entries.
Hence, the preparation of the ledger is the third step in the accounting cycle and is prepared from the journal entries.
See less
A cash discount is a discount allowed to customers when they make payments for the items they purchased. This type of discount is generally based on time. The early the payment is made by the debtors, the more discount they earn. To be more precise cash discount is given to simulate or encourage earRead more
A cash discount is a discount allowed to customers when they make payments for the items they purchased. This type of discount is generally based on time. The early the payment is made by the debtors, the more discount they earn. To be more precise cash discount is given to simulate or encourage early payment by the debtors.
Trade discount is a discount allowed by traders on the list price of the goods to the customer at specified rate. Unlike cash discount, trade discount is based on number of sale i.e, more the sale more the discount earned. This is mainly given on bulk orders by the customers.
To understand trade discount and cash discount let me give you simple example
Mr. X purchased goods from Mr. Y of list price Rs 10,000. Mr. Y allowed a 10% discount to Mr.X on the list price for purchasing goods in bulk quantity. Further, he was provided with cash discount of Rs 500 for making an immediate payment. Therefore the entry for the above transaction in the books of Mr. X would be