The term ‘contra’ means 'opposite'. Therefore, a contra revenue account is an account that is opposite of the revenue accounts of a business i.e. sales account. It has the opposite balance of the revenue account i.e. debit balance. The purpose of the contra revenue account is to ascertain the actuaRead more
The term ‘contra’ means ‘opposite’. Therefore, a contra revenue account is an account that is opposite of the revenue accounts of a business i.e. sales account. It has the opposite balance of the revenue account i.e. debit balance.
The purpose of the contra revenue account is to ascertain the actual amount of sales and record the items which have reduced the sales.
These are the contra revenue accounts commonly seen in businesses:
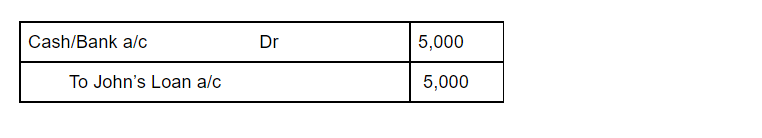
- Sales return account: This account records the amount of goods sold returned by customers. The journal entry for recording sale return is as follow:

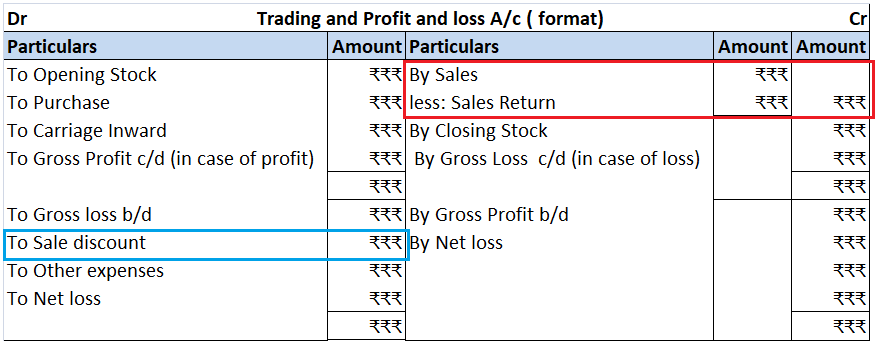
The total sales return is deducted from the sales in the balance sheet. Though being opposite of the sales account, the sale return account is not an expense account. It is considered an indirect loss as it reduces sales.
- Sale Discount account: This account records the amount of discount allowed to customers. The journal entry for recording sale discounts is as follows:

Sales discount is an expense hence it is debited to the profit and loss account.
Sales returns and sales discounts are shown in the trading and profit and loss account in the following manner:

Capital Work in Progress refers to the total cost incurred on a fixed asset that is still undergoing construction as on the balance sheet date. These costs are not allowed to be used as an operating asset until the asset is ready to use. Until the construction of the asset is completed, the costs arRead more
Capital Work in Progress refers to the total cost incurred on a fixed asset that is still undergoing construction as on the balance sheet date. These costs are not allowed to be used as an operating asset until the asset is ready to use. Until the construction of the asset is completed, the costs are recorded as capital work in progress.
Depreciation is the systematic allocation of the cost of an asset over its useful life. Depreciation is charged on an asset from the date it is ready to use. Since Capital Work in Progress is not yet ready to use, depreciation cannot be charged on it.
Example
If a company owns a Machinery worth Rs. 45,000 out of which Rs. 15,000 is part of capital work in progress, then depreciation on such machinery would be calculated only on the part of machinery that is ready to use that is Rs. 30,000 (45,000-15,000).
When an asset is undergoing construction, the journal entry for each expense would be recorded as
Further, when all construction of the above asset is completed, it is transferred to fixed asset account. This would be recorded as
After transfer to Fixed Asset account, depreciation can be calculated and shown as below
If the construction of an asset is complete but has not been put to use till now, depreciation is still calculated as it is ready for use. It can be done through various methods like straight-line method, written down value method etc.
See less