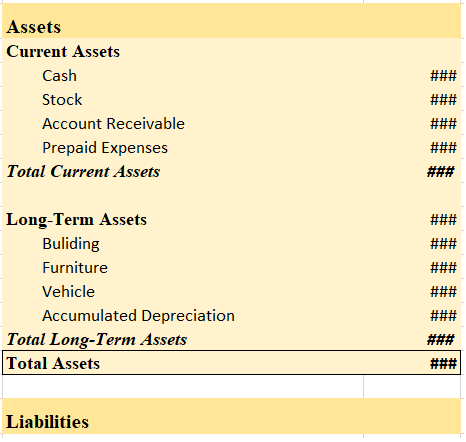
Fictitious assets are the expenses and losses which are yet to be written off, so they appear in the Asset side of the balance sheet of the relevant financial year because expenses and losses have a debit balance. They are not assets in substance. Examples: Business loss ( debit balance of Profit anRead more
Fictitious assets are the expenses and losses which are yet to be written off, so they appear in the Asset side of the balance sheet of the relevant financial year because expenses and losses have a debit balance. They are not assets in substance.
Examples:
- Business loss ( debit balance of Profit and loss A/c )*
- Prepaid expenses
- Discount on the issue of debentures.
- Huge promotional expenditure.
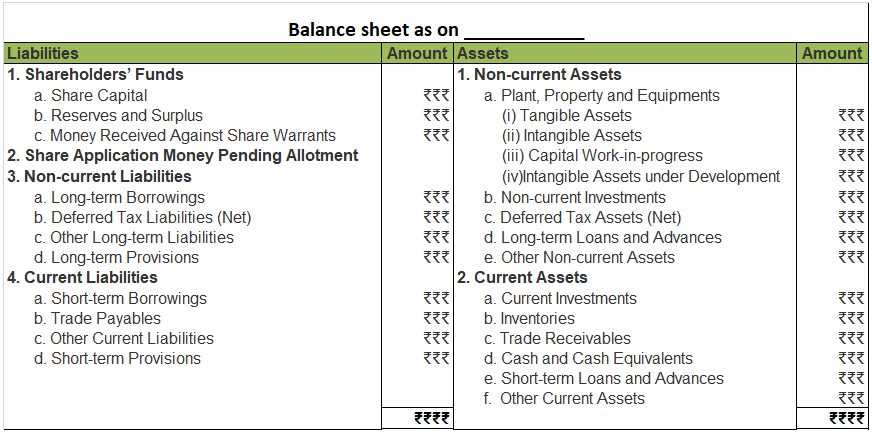
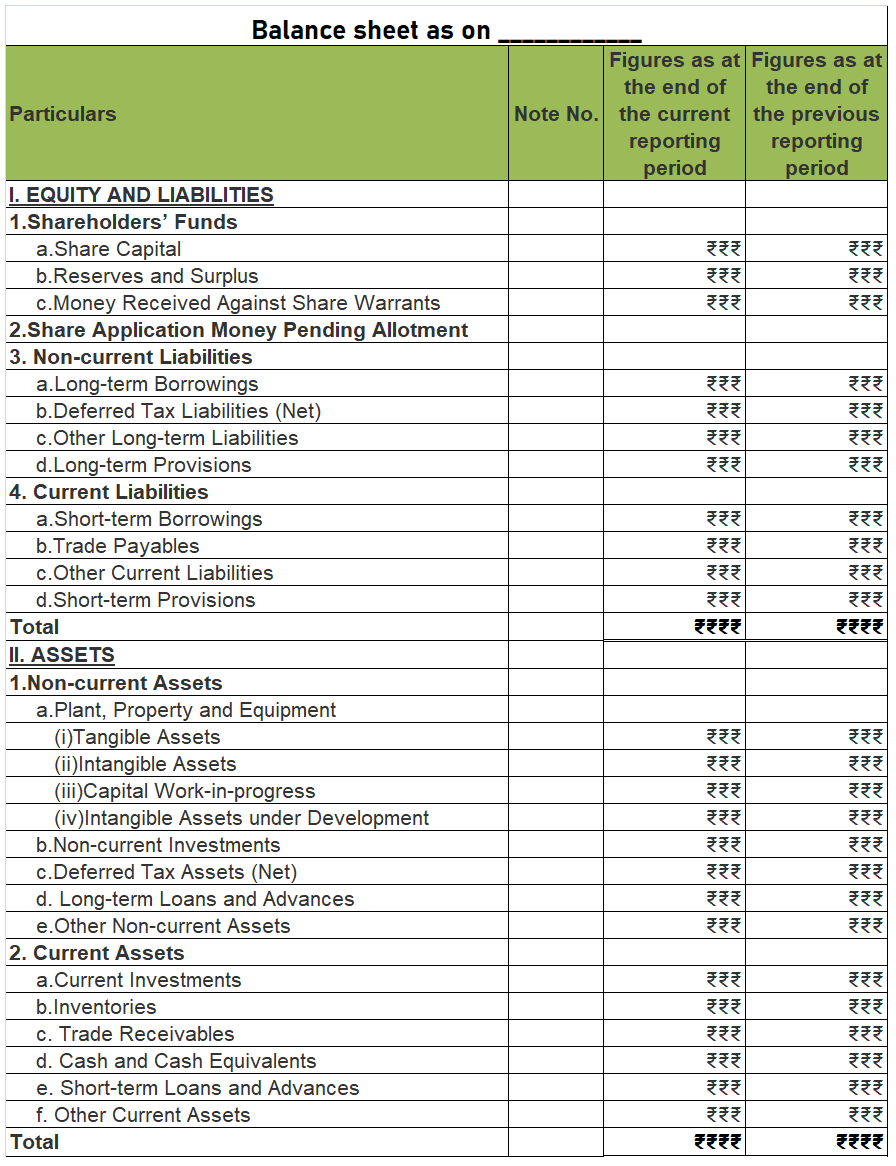
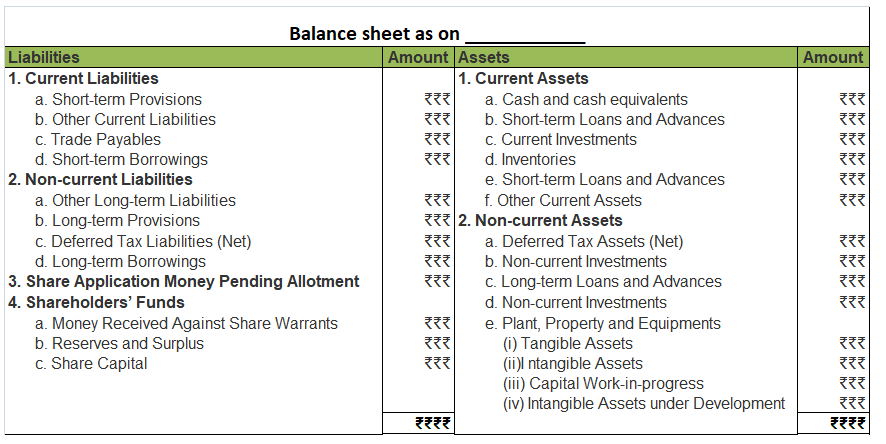
*business loss is shown as a negative figure under the head Reserve and Surplus, when the balance sheet is prepared as per Schedule III of The Companies Act, 2013.
Deferred revenue expenditures are the expenses incurred for which the benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise beyond the current year. Such expenses are huge and are not written off completely in a financial year. The part of the expenditure which is not written off is shown on the assets side of the balance sheet.
Examples:
- Huge advertisement expense.
As you can see, there is some similarity between the two. Deferred revenue expenditure can be called a type of fictitious asset as it is shown in the asset side of the balance sheet but it isn’t an asset.
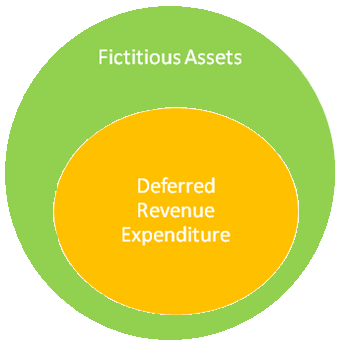
The term ‘fictitious asset’ has a broader meaning than deferred revenue expenditure and also includes the losses such as discounts on the issue of debenture and business loss.
The difference between fictitious assets and deferred revenue expenditure are as follows:
| Fictitious Assets | Deferred Revenue Expenditure | |
| 1 | These are no real assets but expenses and losses that are not completely written off in an F.Y. | These are expenses incurred from which benefits are expected to flow for more than one accounting period. |
| 2 | It has a broader meaning. | It has a narrower meaning. |
| 3 | Examples:- business loss, discount on issue of debentures, prepaid expenses etc. | Examples:- huge promotional expenditure etc. |

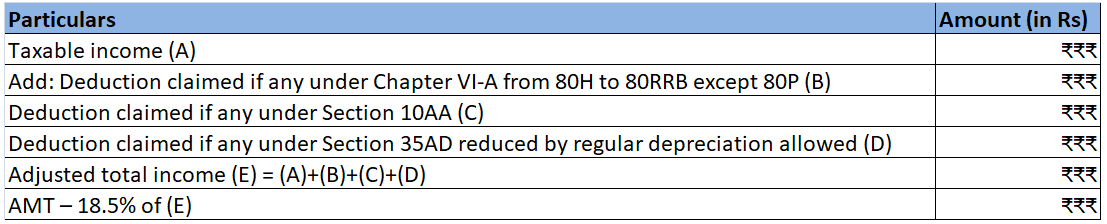
The journal entry for the opening stock will be: Particulars Amt Amt Trading A/c INR To Opening Stock A/c INR (Being opening stock transferred to Trading A/c) Opening stock is the value of inventory that is available with the company for sale at the beginning of the accounting period. ORead more
The journal entry for the opening stock will be:
Opening stock is the value of inventory that is available with the company for sale at the beginning of the accounting period. Opening stock may include stock of raw material, semi-finished goods, and finished goods. It is a part of the cost of sales.
Closing stock is the value of unsold inventory left with the company at the end of the year. The previous year’s closing stock is the current year’s opening stock.
Trading Account is a nominal account. According to the golden rules of accounting, the nominal account is the account where “Debit” all expenses and losses, and “Credit” all income and gains.
In the above journal entry, the opening stock account is credited because it is the balance that is carried forward from the previous year and carried forward with the aim of selling it and gaining profit from it. The trading account here is debited as opening stock is carried forward to the next year from the trading account only.
According to modern rules of accounting, “Debit entry” increases assets and expenses, and decreases liability and revenue, a “Credit entry” increases liability and revenues, and decreases assets and expenses.
Here, Trading A/c is debited because an expense is incurred while bringing stock into the business. Opening Stock A/c is credited because indirectly it is creating a source of income for the business.
The formula for calculating opening stock is as follows:
Opening Stock = Cost of Goods Sold + Closing Stock – Purchases
For example, AB Ltd. started a new accounting period for dairy products and introduced opening stock worth Rs.1,00,000 in the business.
Here, the journal entry will be,