Any person, company, or organization that owes us money is a debtor. The amount that is owed to us is called debt. When you are unsure if a debtor is going to pay back the amount owed to you, then a provision for doubtful debts is created. Here, the debtor may or may not pay back the amount owed. WhRead more
Any person, company, or organization that owes us money is a debtor. The amount that is owed to us is called debt. When you are unsure if a debtor is going to pay back the amount owed to you, then a provision for doubtful debts is created. Here, the debtor may or may not pay back the amount owed. When the debts owed to us is irrecoverable, it is termed as bad debts.
Provision for doubtful debts may become a bad debt at some point. Usually, companies keep a small portion of their debtors as a provision for doubtful debts in accordance with the prudence concept that tells us to account for all possible losses. Provision for doubtful debts is a liability whereas bad debts are recorded as an expense.
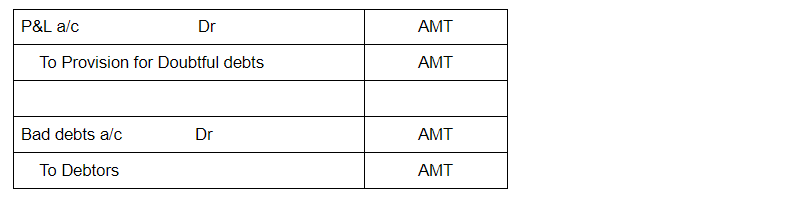
Journal entries for Doubtful debts and bad debts are as follows:
EXAMPLE
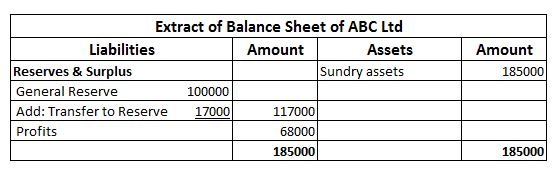
If the balance in the debtors’ account shows an amount of Rs 20,000 and 5% of debtors are treated as doubtful, then Rs 1,000 is recorded as a provision for doubtful debts. This amount is deducted from debtors in the balance sheet.
Now if Rs 400 was recorded as actual bad debts, then it is deducted from the provision for doubtful debts instead of debtors. Further another 400 is added back to provision for doubtful debts to maintain the percentage.
See less
The term ‘bad debt’ and ‘write off’ are often used together in a sentence but they have different meanings. First, we will discuss them in brief to understand the differences between them. Bad debts We know, debtors for a business are their assets because the business has the right to receive moneyRead more
The term ‘bad debt’ and ‘write off’ are often used together in a sentence but they have different meanings. First, we will discuss them in brief to understand the differences between them.
Bad debts
We know, debtors for a business are their assets because the business has the right to receive money from the debtors due to the goods supplied to them.
But if due to circumstances, there appears no probability that the amount due to one or more debtors will be realised to the business, then such debts are categorised as bad debts.
In short, bad debts refer to the amount of money that will not be received from some debtors of the business due to some circumstances like insolvency of debtor etc.
Bad debt is deducted from debtors account by the following journal entry:
As bad debts are losses to a business, it is ultimately written off from the profit and loss account.
Write off
In layman terms, write off means to deduct something out from something. In accounting, write off means to deduct or reduce value of assets by crediting it to a liability account which is usually a reserve account or the profit and loss account.
It also refers to the elimination of an item from the books of accounts particularly losses and expenses.
Generally, writing off is associated with the following:
Write off can be done in one of the following methods:
Hence, the following differences can be observed between bad debts and write off or writing off:

See less