Debit balance means excess of credit side over debit side. For Example- At the beginning of the year the debit balance of trade receivables is 3,000 and there is a decrease(credit) of trade receivables of 1,000 during the year and an increase(debit) of trade receivables of 4,000 then at the end therRead more
Debit balance means excess of credit side over debit side.
For Example- At the beginning of the year the debit balance of trade receivables is 3,000 and there is a decrease(credit) of trade receivables of 1,000 during the year and an increase(debit) of trade receivables of 4,000 then at the end there will be a debit balance of 6,000 of trade receivables at the end
A Debit balance basically signifies all expenses and losses and all positive balances of assets. The debit balance increases when any asset increases and decreases when any asset decreases.
Assets
All the assets that appear in the balance sheet always have a debit balance. The debit balance under it will increase as it debits. Some of these assets can be illustrated below -:
- Cash and Bank Balance: Cash and Bank Balance means the amount that is held by a person in physical form or in a current/savings account.
- Property, Plant, and Equipment- Property Plant, and Equipment means assets that are used for the production of goods and services.
- Account Receivables– Account Receivables means the amount that is due from debtors to whom goods were sold at credit for a specified time period.
- Inventory – Inventory means goods that are used in the normal course of business.
- Investments– Investments are the amount invested in other companies from which they were expecting returns in future periods.
Expenses and Losses
All expenses that appear on the debit side of the P&L account have a debit balance in their accounts.
For eg-: A rent of 10,000 is given to the landlord under which the work has been done by the entity.
For eg-: A depreciation of 10% is there on an asset of 12,000 will result in a debit balance under depreciation in the P&L Account.
Some of the following expenses can be illustrated below
- Rent- Rent means a property that an entity takes on lease for business purpose and pay a certain amount to the landlord for such lease.
- Depreciation– Depreciation means a fall in the value of an asset due to its usage every year
- Loss on Sale of an asset- Loss on the Sale of an Asset means the sale amount of the asset is less than its WDV
- Printing and stationery– Printing and Stationery means the paperwork or anything related to stationery used for business purposes
- Audit fees– Audit fees are the amount which is given to an auditor for auditing the financials of an entity
- Salaries and Wages– Salaries and Wages are the amount given to employees for the work they have done for the entity
- Insurance– Insurance means a premium given by an entity for insurance done by them
- Advertising– Advertising means any promotion that a company does of its product to increase its revenue
So after seeing all the above points we can conclude that the debit balance includes all the expenses that are in the P&L account and all the assets that are there in the Balance sheet. So its balance increases when there is an increase in its account.
CREDIT BALANCE
Credit balance means excess of credit side over debit side.
For example, At the beginning of the year, the credit balance of trade payable is 3,000 and there is a debit of trade payable of 1,000 during the year and an increase(credit) of trade payable of 4,000 then at end there will be a credit balance of 6,000 for trade payable at the end
.A Credit balance signifies all income and gains and all liabilities and capital that is there in business.
Liabilities
- Account Payables
- Bank Overdraft
- Bonds
- Income Tax Payables
- Notes Payable
- Deferred Tax Liability
Income and Gains
- Interest Received
- Dividend Received
- Rent Received
- Gains on Sale of Capital Gains
See less


Definition Bad debts are a debt owed to an enterprise that is considered to be irrecoverable or we can say that it is owed to the business that is written off because it is irrecoverable. Sometimes debtors are unable to pay the amount due either partially or fully. the amount that is not receivableRead more
Definition
Bad debts are a debt owed to an enterprise that is considered to be irrecoverable or we can say that it is owed to the business that is written off because it is irrecoverable.
Sometimes debtors are unable to pay the amount due either partially or fully. the amount that is not receivable is a loss and is called bad debt.
Bad debts are neither assets nor liabilities they are expenses that are debited to the profit and loss account and reduced from debtors in the balance sheet.
For example loans from banks are declared as bad debt, sales made on credit and amounts not received from customers, etc.
Related terms
So there are a few related terms whose meanings you should know
Accounting methods
There are two methods for accounting for bad debts which are mentioned below:-
Accounting treatment
Now let me try to explain to you the accounting treatment for bad debts which is as follows :
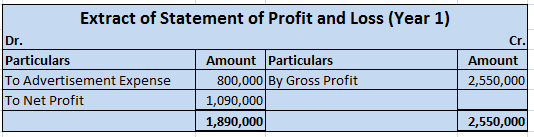
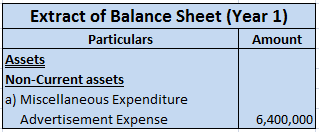
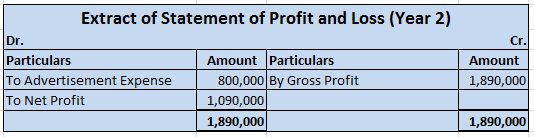
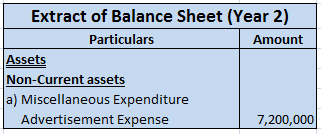
Now let me show you the extract of the profit and loss account and balance sheet showing bad debts and bad debts recovered which are as follows:-

See less