The terms outstanding expenses and accrued expenses are two accounting terms which are often used interchangeably. However, these two terms are not the same and have different meanings. The difference between these two terms is given below: What are Outstanding expenses? As the name suggests, outstaRead more
The terms outstanding expenses and accrued expenses are two accounting terms which are often used interchangeably. However, these two terms are not the same and have different meanings. The difference between these two terms is given below:
What are Outstanding expenses?
As the name suggests, outstanding expenses are the expenses that are due but have not been paid yet. It means that the business is supposed to pay the amount due but it has not paid the same at the end of the accounting period.
Outstanding expenses are recognized as a current liability because the business is liable to pay such expenses. These expenses are recorded in the books of accounts but the payment is still pending.
Some examples of outstanding expenses are:
- The electricity bill is due for the month of January but has not yet been paid on 31st January.
- Salaries of employees of 50,000 is due for the month of March but have not been paid yet by the business.
What are Accrued expenses?
Accrued expenses are the expenses that a business has incurred during the accounting period but they have not yet been recorded in the books of accounts because the bill has not yet been received or the payment is not due yet.
The concept of Accrued expenses helps in complying with the accrual basis of accounting which says that the expense shall be recognised at the time it occurs regardless of the fact that payment is received or not.
Examples of accrued expenses are:
- The electricity bill for December is received in the month of January. However, it shall be recognised as an expense in the month of December.
- The salaries of the employees for the month of April are paid in May. However, this expense shall be recognized in April.
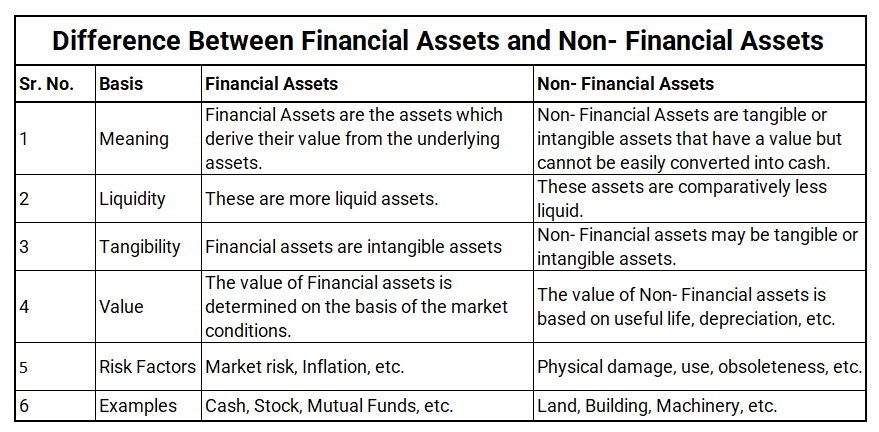
Key differences between outstanding expenses and accrued expenses
To summarise the above discussion, the key differences between outstanding expenses and accrued expenses are given in the table below:
See less


To understand the difference in Revenue recognition under IFRS and GAAP , it is important to understand what are IFRS and GAAP. Both of these are accounting standards accepted globally. These are discussed below: What is IFRS? IFRS is a set of accounting standards developed by the International AccRead more
To understand the difference in Revenue recognition under IFRS and GAAP , it is important to understand what are IFRS and GAAP. Both of these are accounting standards accepted globally. These are discussed below:
What is IFRS?
IFRS is a set of accounting standards developed by the International Accounting Standards Board. These standards are globally accepted accounting standards.
They were developed and implemented with the objective of providing a consistent, transparent and reliable framework for the presentation and reporting of financial statements.
IFRS ensure uniformity and this helps in comparability of financial statements across the companies of different countries.
Some examples of IFRS Standards are : IFRS 2 – Share based payments, IFRS 9 – Financial Instruments, IFRS 16 – Leases, etc.
What is GAAP?
GAAP stands for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. GAAP is primarily used in the USA. These are a set of accounting principles, rules and procedures which are crucial for providing consistency and transparency in the presentation and reporting of financial statements.
Some examples of GAAP Standards are: ASC 606: Revenue Recognition, ASC 842: Leases, ASC 740: Income Taxes, etc.
Difference in Revenue Recognition under IFRS and GAAP
Though both of these standards have the main goal of promoting consistency and uniformity, there are certain differences in the Revenue Recognition under IFRS and GAAP.
This is because of the fact that the nature of IFRS and GAAP is different as IFRS is more principle- based and GAAP is rule based.
See less