Here are 10 examples of accounting entries: A company purchases $500 worth of office supplies on credit from a supplier. Office supplies expense account would be debited Accounts payable would be credited A firm receives $1,000 in cash from a customer for services rendered. In this case, CashRead more
Here are 10 examples of accounting entries:
- A company purchases $500 worth of office supplies on credit from a supplier.
- Office supplies expense account would be debited
- Accounts payable would be credited
- A firm receives $1,000 in cash from a customer for services rendered. In this case,
- Cash account would be debited
- Service revenue account would be credited
- A business pays $250 in salaries to its employees.
- A debit would be made to the salaries expense account
- A credit would be made to the cash account
- A business borrows $5,000 from a bank and receives the funds as a loan. The entry would be,
- A debit to the bank account
- A credit to the loan payable account
- A company sells $800 worth of inventory to a customer for cash.
- The entry would be a debit to the cash account
- A credit to the sales revenue account
- A firm purchases $3,000 worth of equipment on credit from a supplier.
- The entry would be a debit to the equipment account
- A credit to the supplier’s account
- A company incurs $500 in advertising expenses for a new marketing campaign (cash).
- The entry would be a debit to the advertising expense account
- A credit to the cash account
- A firm collects $1,200 from a customer. The entry would be,
- A debit to the cash account
- A credit to the customer’s account
- A business pays $700 in rent for its office space. The entry would be,
- A debit to the rent expense account
- A credit to the cash account
- An organization pays off a $2,000 loan to the bank. The entry would be,
- A debit to the loan payable account
- A credit the cash account
I also found a long list of example journal entries and a free PDF to download here.
See less


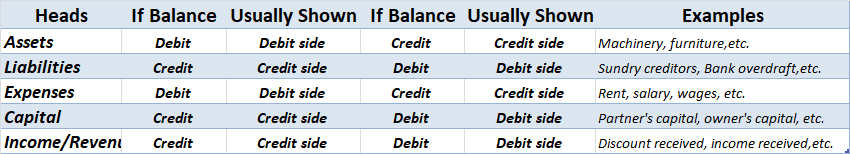
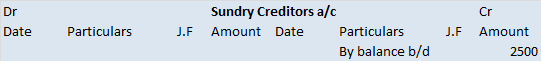
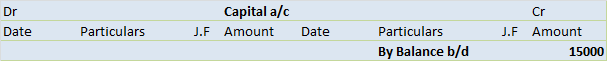
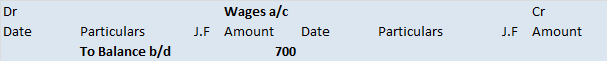
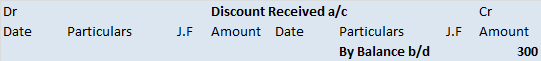
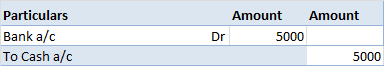
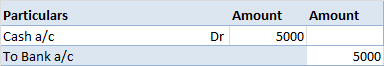
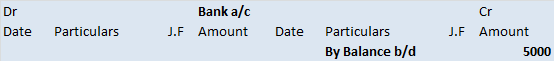
 The trial balance shows the opening balance of various accounts. Now posting them in ledger accounts.
The trial balance shows the opening balance of various accounts. Now posting them in ledger accounts.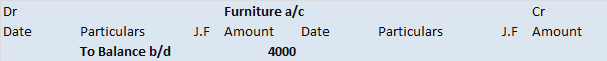
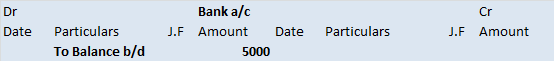
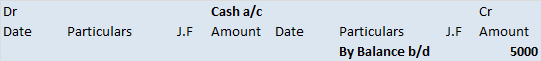
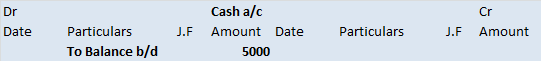
Capitalize in Accounting The term 'capitalized' in accounting means to record an expenditure as an asset on the balance sheet. Capitalization takes place when a business buys an asset that has a useful life. The cost of the relevant asset is then allocated to expense over its useful life i.e charginRead more
Capitalize in Accounting
The term ‘capitalized’ in accounting means to record an expenditure as an asset on the balance sheet. Capitalization takes place when a business buys an asset that has a useful life. The cost of the relevant asset is then allocated to expense over its useful life i.e charging depreciation, etc. This means that the relevant expenditure will appear on the balance sheet instead of the income statement. The capitalizing of the expenses is a benefit for the company as the assets bought by them for the long-term are subjected to depreciation and capitalizing expenses can amortize or depreciate the costs. This process is called capitalization.
In order to capitalize any expense, we’ll have to make sure it meets the criteria stated below.
The assets exceeding the capitalization limit
The companies set a capitalization limit, below which the expenses are considered too immaterial to be capitalized. Therefore, the limit is supposed to be followed and considered as it controls the capitalization of the expenses. Generally, the capitalization limit is $1,000.
The assets have a useful life
The companies also seek to generate revenues for a long period of time. Thus, the asset should have a long and useful life at least a year or more. Thereby, the business can record it as an asset and depreciate it over its valuable life.
Most of the important principles of capitalization in accounting are from the matching principle.
Matching Principle
The matching principle states that the expenses in the accounting should be recorded when they are incurred and not when the payment is made. This helps the business identify the amounts spent to generate revenue.
For e.g, the company bought machinery for manufacturing goods with more efficiency. It is supposed to have a useful life for a period of over 10 years. Instead of expensing the entire cost of the machinery, the company will write off (depreciated) the cost of the asset over its useful life i.e 10 years. Therefore, the asset will be written off as it is used and these types of assets are automatically used as capitalized assets.
Benefits of Capitalization
Capitalization is of course recording expenses as an asset but this indeed has benefits.
See less