When a company earns profit, it distributes a proportion of its income to its shareholders, and such distribution is called the dividend. The dividend is allocated as a fixed amount per share and shareholders receive dividends proportional to their shareholdings. However, a company can only pay diviRead more
When a company earns profit, it distributes a proportion of its income to its shareholders, and such distribution is called the dividend. The dividend is allocated as a fixed amount per share and shareholders receive dividends proportional to their shareholdings.
However, a company can only pay dividends out of its current year profits or retained earnings (profits of the company that are not distributed as dividend and retained in the business is called retained earnings) of previous years but not out of capital.
Dividends can be paid to shareholders in the form of
- Cash
- dividend re-investing plan of the company
- future shares
- share repurchase.
For companies, payment of regular dividends boosts the morale of the shareholders, investors trust the companies more and it reflects positively on the share price of the company.
For example, Nestle in India paid an interim dividend of 1100.00% to its shareholders in 2021.
The journal entry for dividend paid is
| Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| Retained Earnings A/c Dr. | Amt | |
| To Cash A/c | Amt |
According to the golden rules of accounting-
- Retained earnings is a credit account by nature and since dividends are paid from retained earnings resulting in a deduction of the account, we debit
- Cash is credited because the account is debit in nature and since dividends are paid in cash it’s credited to present the deduction in the account.
According to modern rules of accounting-
- Since cash is decreasing, we credit
- Since retained earnings are decreasing and it is a part of capital it should be
For example-
A company paid a dividend of 25 crores to its shareholders in cash, the journal entry according to golden rules will be-
| Particulars | Debit
(in crores) |
Credit
(in crores) |
| Retained Earnings A/c (Dr.) | 25 | |
| To Cash A/c | 25 |
See less


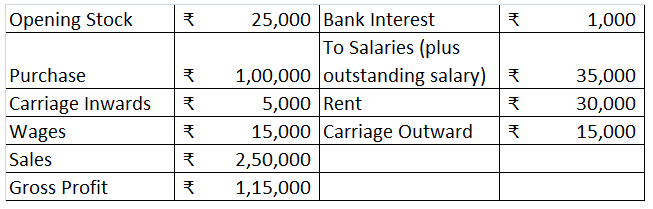
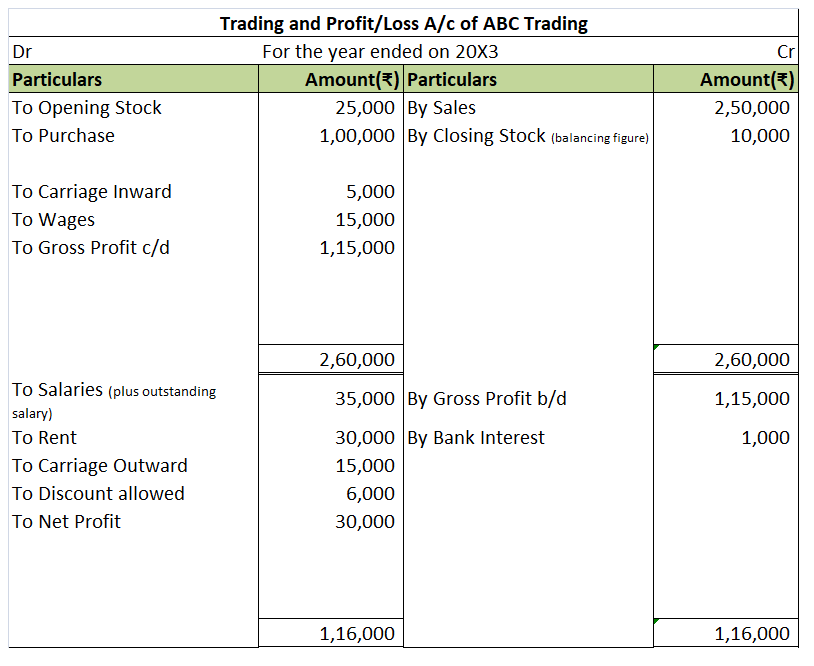
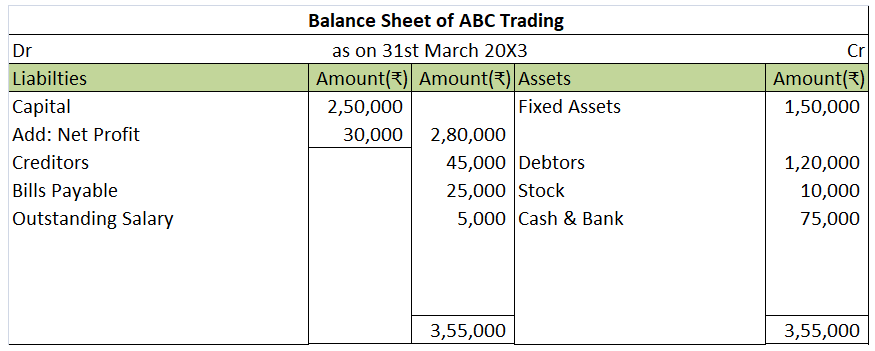
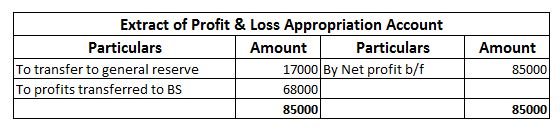
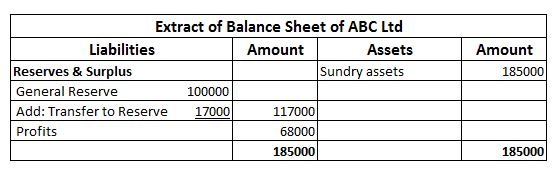
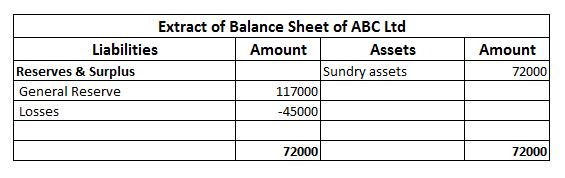

External liabilities are the amounts which a business is obliged to pay to the outsiders (who are not owners of the business). Here is the list of external liabilities:- Accounts payable ( trade creditors and bills payables) Loan taken from outsiders Loan from bank Debentures Public deposits accepteRead more
External liabilities are the amounts which a business is obliged to pay to the outsiders (who are not owners of the business).
Here is the list of external liabilities:-
The list is not exhaustive.
Just for more understanding, internal liabilities are those liabilities which a business is supposed to pay back to its owners. Such as capital balance, profit surplus etc.
See less