When the Accumulated depreciation account is not maintained, the journal entry for vehicle depreciation shall be Particulars Debit Credit Depreciation a/c Dr. (xxx) To Vehicle a/c (xxx) (Being DepreciationRead more
When the Accumulated depreciation account is not maintained, the journal entry for vehicle depreciation shall be
| Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| Depreciation a/c Dr. | (xxx) | |
| To Vehicle a/c | (xxx) | |
| (Being Depreciation charge on Vehicle made) |
For example, let us assume that a vehicle (Bike) was purchased on 1st April 2019 with INR. 2,50,000, the rate of depreciation is 15% and also the Company follows the straight-line method of calculating depreciation.
Then the journal entries shall be,
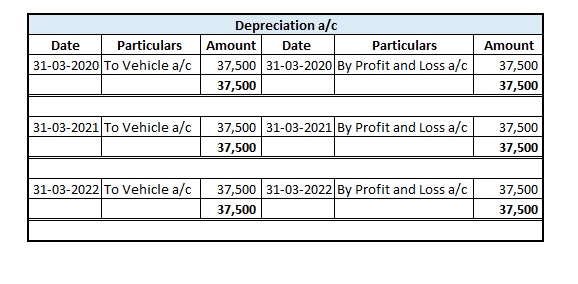
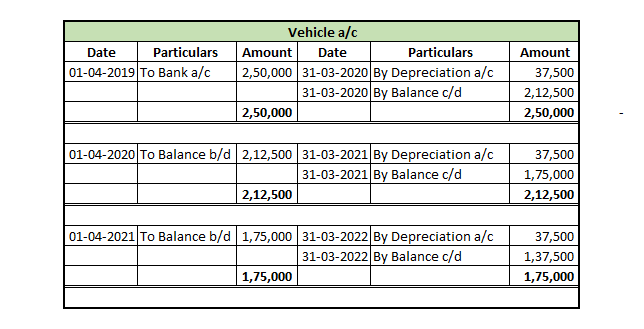
The depreciation charge for the 1st Year
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| 31-03-2020 | Depreciation a/c Dr. | 37,500 | |
| To Vehicle a/c | 37,500 | ||
| (Being Depreciation made on Vehicle) |
The depreciation charge for the 2nd Year
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| 31-03-2021 | Depreciation a/c Dr. | 37,500 | |
| To Vehicle a/c | 37,500 | ||
| (Being Depreciation made on Vehicle) |
The depreciation charge for the 3rd Year
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| 31-03-2022 | Depreciation a/c Dr. | 37,500 | |
| To Vehicle a/c | 37,500 | ||
| (Being Depreciation made on Vehicle) |
The respective ledger accounts for all three years are given below:
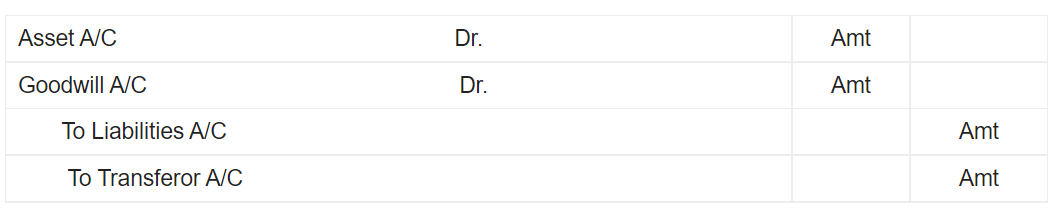
When the Accumulated depreciation account is maintained, the journal entry for vehicle depreciation shall be
| Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| Depreciation a/c Dr. | (xxx) | |
| To Accumulated depreciation a/c | (xxx) | |
| (Being Depreciation charge on Vehicle made) |
Taking the above said example,
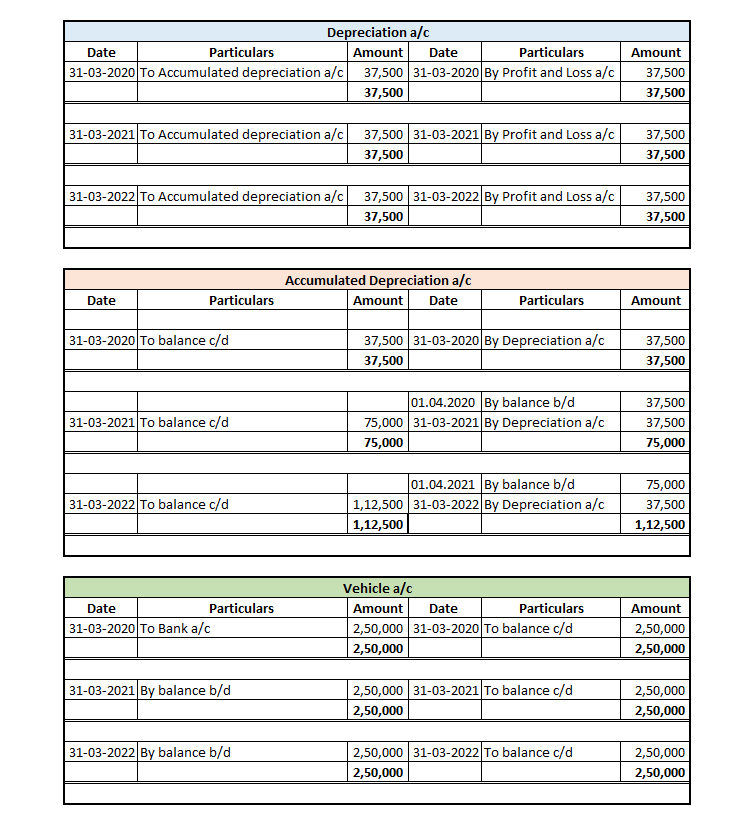
The depreciation charge for the 1st Year
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| 31-03-2020 | Depreciation a/c Dr. | 37,500 | |
| To accumulated depreciation a/c | 37,500 | ||
| (Being Depreciation made on Vehicle) |
The depreciation charge for the 2nd Year
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| 31-03-2021 | Depreciation a/c Dr. | 37,500 | |
| To accumulated depreciation a/c | 37,500 | ||
| (Being Depreciation made on Vehicle) |
The depreciation charge for the 3rd Year
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| 31-03-2021 | Depreciation a/c Dr. | 37,500 | |
| To accumulated depreciation a/c | 37,500 | ||
| (Being Depreciation made on Vehicle) |
The respective ledger accounts for all three years are given below:
See less


Shareholder's Equity Meaning - Shareholder's Equity is the amount invested into the Company. It represents the Net worth of the Company. It is also where the owners have the claim on the Assets after the Debts are settled. It Calculation of Shareholder's Equity Method 1 Shareholder's Equity = TotalRead more
Shareholder’s Equity
Meaning – Shareholder’s Equity is the amount invested into the Company. It represents the Net worth of the Company. It is also where the owners have the claim on the Assets after the Debts are settled. It
Calculation of Shareholder’s Equity
Method 1
Shareholder’s Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
Method 2
Shareholder’s Equity = Share Capital + Retained Earnings – Treasury Stock/Treasury Shares
Components of the Shareholder’s Equity
From the above Method 1, it can be understood that shareholder’s equity comprises of
Net Assets = Current Assets + Non-current Assets, reduced by
Net liabilities = Current liabilities + Long-term liabilities
where Long-term liabilities = Long-term debts + Deferred long-term liabilities + Other liabilities
Also from the method 2,
Share Capital = Outstanding shares + Additional Paid-up share capital
Retained Earnings are the sum of the company’s earnings after paying the dividends
Treasury stocks = Shares repurchased by the company
Example of Shareholder’s Equity
The shareholder’s Equity is represented in the Balance Sheet as below;
See less