Here are 10 examples of accounting entries: A company purchases $500 worth of office supplies on credit from a supplier. Office supplies expense account would be debited Accounts payable would be credited A firm receives $1,000 in cash from a customer for services rendered. In this case, CashRead more
Here are 10 examples of accounting entries:
- A company purchases $500 worth of office supplies on credit from a supplier.
- Office supplies expense account would be debited
- Accounts payable would be credited
- A firm receives $1,000 in cash from a customer for services rendered. In this case,
- Cash account would be debited
- Service revenue account would be credited
- A business pays $250 in salaries to its employees.
- A debit would be made to the salaries expense account
- A credit would be made to the cash account
- A business borrows $5,000 from a bank and receives the funds as a loan. The entry would be,
- A debit to the bank account
- A credit to the loan payable account
- A company sells $800 worth of inventory to a customer for cash.
- The entry would be a debit to the cash account
- A credit to the sales revenue account
- A firm purchases $3,000 worth of equipment on credit from a supplier.
- The entry would be a debit to the equipment account
- A credit to the supplier’s account
- A company incurs $500 in advertising expenses for a new marketing campaign (cash).
- The entry would be a debit to the advertising expense account
- A credit to the cash account
- A firm collects $1,200 from a customer. The entry would be,
- A debit to the cash account
- A credit to the customer’s account
- A business pays $700 in rent for its office space. The entry would be,
- A debit to the rent expense account
- A credit to the cash account
- An organization pays off a $2,000 loan to the bank. The entry would be,
- A debit to the loan payable account
- A credit the cash account
I also found a long list of example journal entries and a free PDF to download here.
See less

Profitability ratios measure how profitable a company is and are used to assess its performance and efficiency. Based on the income statement and balance sheet of a company, these ratios are calculated. In terms of profitability ratios, there are several types, each providing a different viewpoint.Read more
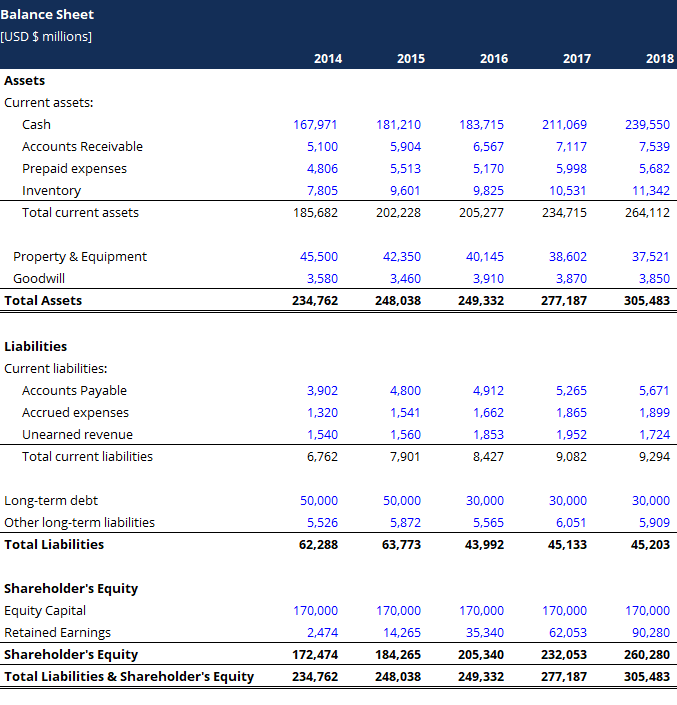
Profitability ratios measure how profitable a company is and are used to assess its performance and efficiency. Based on the income statement and balance sheet of a company, these ratios are calculated.
In terms of profitability ratios, there are several types, each providing a different viewpoint.
The following are some common profitability ratios:
Gross profit margin: This ratio measures the percentage of revenue that remains after the cost of goods sold has been deducted. Producing and selling efficiently is indicated by this metric.
Net profit margin: An organization’s net profit margin is the portion of revenue left after all expenses have been deducted. A company’s profitability is measured by this indicator.
Return on assets (ROA): This ratio measures how profitable a company’s assets are. In other words, it indicates how effectively a company generates profits from its assets.
Return on equity (ROE): This ratio measures the profitability of a company’s equity. It shows how effectively a company generates profits from its shareholders’ investments.
Analysts and investors use profitability ratios to evaluate a company’s performance and profitability ability.
An investor or analyst can evaluate a company’s relative strength and identify potential opportunities or risks by comparing its profitability ratios with its peers or its industry averages.
See less