Wages Outstanding Wages and Salaries Director’s Remuneration Advance Payment of Wages All of the Above
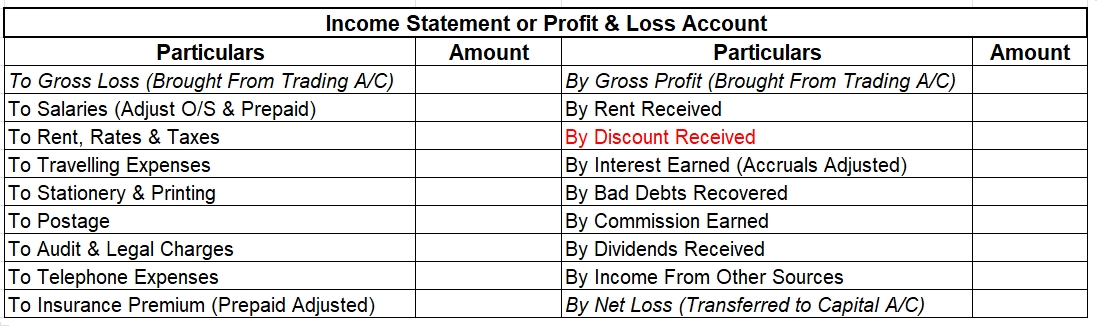
The profit earned by an entity is determined through the profit and loss account. All the expenses are recorded on the debit side of the profit and loss account while all the incomes are recorded on the credit side. The profit is shown as the credit balance of profit and loss A/c. When the sum of itRead more
The profit earned by an entity is determined through the profit and loss account. All the expenses are recorded on the debit side of the profit and loss account while all the incomes are recorded on the credit side.
The profit is shown as the credit balance of profit and loss A/c. When the sum of items on the debit side of a profit and loss account is less than the sum of those on the credit side, it implies profit while when the sum of the items on the credit side is less than the sum of those on the debit side, it implies a loss for the entity.
The Reason for Credit
Profit is recorded as an increase in equity
To understand the reason why profit is recorded as a credit balance, we must first understand the basic principle of debit and credit.
The basic principle of debits and credits is that debits increase asset accounts and decrease liability and equity accounts while credits decrease asset accounts and increase liability and equity accounts.
The revenue that a company earns is credited to the income account and increases equity.
The expenses that a company incurs to earn that revenue are debited to the expense account and decrease equity.
The difference between revenue and expenses is the profit, which is recorded as an increase in equity.
Increase in equity due to revenue – decrease in equity due to expense = profit
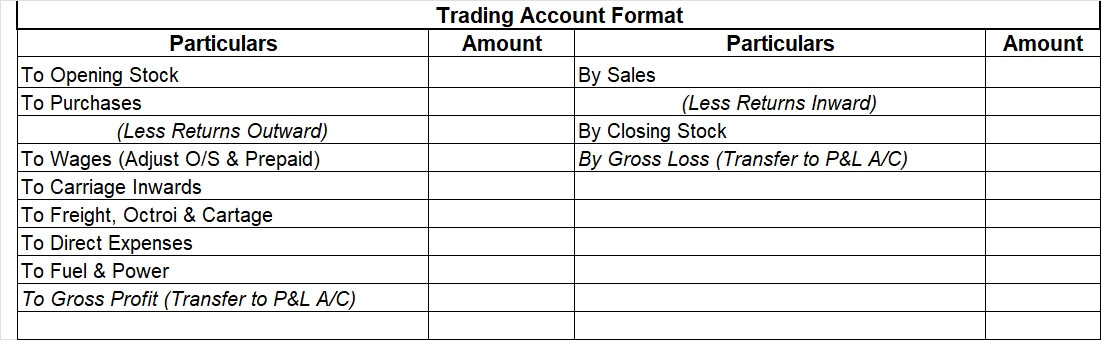
Gross Profit Vs Net Profit
Revenue is the total income that a business or profession earns. Profit is the excess revenue that remains after reducing all expenses from it.
Gross profit is the profit that a company earns after reducing the cost of goods sold from sales revenue while net profit is the profit that a business earns after reducing the total of all its direct and indirect expenses from its direct as well as indirect allowable business income.
Conclusion
The basic principle of debit and credit governs the classification of profit as a debit or credit. Since profit increases our equity, it is a credit.
In the case of a company, it belongs to the shareholders. It is usually recorded in the retained earnings account. Profit can be reinvested in the business or can be distributed as a dividend. In the case of a sole proprietorship, the profit belongs to the owner and is recorded in the owner’s capital account.
See less
The correct answer is option B. Wages and salaries are debited to the trading account. The trading account helps us to determine the Gross Profit Or Loss that a company earns or incurs by carrying on its core manufacturing or trading activities. Let us discuss the above items and their treatments inRead more
The correct answer is option B. Wages and salaries are debited to the trading account.
The trading account helps us to determine the Gross Profit Or Loss that a company earns or incurs by carrying on its core manufacturing or trading activities.
Let us discuss the above items and their treatments in the final accounts one at a time:
Wages Outstanding
Firstly, “wages outstanding” is not debited into the trading account. It is a liability that is shown in the balance sheet.
Outstanding wages imply remuneration due to be paid to the workers for the services they have already rendered to the business.
Since the company has already received the service, it becomes a legal obligation for it to pay the wages to the workers for those services. Hence, outstanding wages are a liability.
Wages and Salaries
Wages and Salaries are debited to the trading account.
Wages Vs Salaries
Let us understand the difference between wages and salaries. Wages are the regular payments that are made daily, weekly or fortnightly. Such payments are mostly made to factory workers.
Salaries, on the other hand, are assumed to imply the remuneration paid to office workers and sales staff.
Wages are debited to the trading account, while salaries are debited to the Profit and Loss account.
Director’s Remuneration
No, the director’s remuneration is not debited to the trading account. This is because director’s generation is a business expense. It is a kind of salary provided to the director for the services rendered by him to the company.
Directors’ remuneration refers to compensation the company gives to its directors for the services rendered. It is debited to the Profit and Loss Account.
Advance Payment of Wages
No, advance payment of wages is not debited to a trading account. It is shown by reducing it to wages. Advance payment of wages implying paying remuneration to the workers before the commencement of the period for which the wages relate to.
However, one must note that if both wages and prepaid wages appear within the trial balance, then only the figure written against wages would appear in the trading account. There would be no treatment for prepaid wages.
Let us consider a scenario where wages of amount 5,000 is appearing inside trial balance. Outside the trial balance, the following information is provided
In the above case, the total wages to be debited to the trading account would be 5,000 + 1,000 – 2,000 = 4,000
Significance of the Final Accounts
See less