Definition The trial balance is a list of all the closing balances of the general ledger at the end of the year. Or in other words, I can say that it is a statement showing debit and credit balances. A trial balance is prepared on a particular date and not on a particular period. Importance As the tRead more
Definition
The trial balance is a list of all the closing balances of the general ledger at the end of the year. Or in other words, I can say that it is a statement showing debit and credit balances.
A trial balance is prepared on a particular date and not on a particular period.
Importance
As the trial balance is prepared at the end of the year so it is important for the preparation of financial statements like balance sheet or profit and loss
Purpose of trial balance which are as follows:
-
- To verify the arithmetical accuracy of the ledger accounts
- This means trial balance indicates that equal debits and credits have been recorded in the ledger accounts.
- It enables one to establish whether the posting and other accounting processes have been carried out without any arithmetical errors.
-
- To help in locating errors
- There can be some errors if the trial balance is untallied therefore to get error-free financial statements trial balance is prepared.
-
- To facilitates the preparation of financial statements
- A trial balance helps us to directly prepare the financial statements and then which gives us the right to not look or no need to refer to the ledger accounts.
Preparation of trial balance
-
- To verify the correctness of the posting of ledger accounts in the terms of debit credit amounts periodically, a periodic trial balance may be prepared ( say ) at the end of the month or quarter, or half year.
-
- There is no point in denying that a trial balance can be prepared at any time.
-
- But it should at least be prepared at the end of the accounting period to verify the arithmetical accuracy of the ledger accounts before the preparation of financial statements.
Methods of preparation
- Balance method
- Total amount methods
These are two methods that you can use to prepare trail balance, now let me explain to you in detail about these methods which are as follows:-
Balance method
- The balances of all the accounts ( including cash and bank account ) are incorporated in the trial balance.
- When ledger accounts are balanced only this method can be used.
- This method is generally used by accountants for preparation of the financial statements.
Total amount method
- Under this method, the total amount of debit and credit items in each ledger account is incorporated into the trial balance.
- This method can be used immediately after the completion of posting from the books of the original entry ledger.
Steps to prepare a trial balance
- First, we need to decide the method to opt for the preparation of the trial balance which is mentioned above.
- Then once opted, collect all the balances as per the method adopted and prepare accordingly by posting the debit and credit side of the trial balance.
- After this process arrange all the accounts in order of their nature (assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses ).
- Then you have to total debit and credit balances separately.
- After the above steps if there is any difference between the total debit and credit side balances then that is adjusted through the suspense account.
A suspense account is generated when the above case arises that is trial balance did not agree after transferring the balance of all ledger accounts including cash and bank balance.
And also errors are not located in timely, then the trial balance is tallied by transferring the difference between the debit and credit side to an account known as a suspense account.
Rules of trial balance
When we prepare a trial balance from the given list of ledger balances, the following rules to be kept in mind that are as follows :
- The balance of all
- Assets accounts
- Expenses accounts
- Losses
- Drawings
- Cash and bank balances
Are placed in the debit column of the trial balance.
- The balances of
- liabilities accounts
- income accounts
- profits
- capital
Are placed in the credit column of the trial balance.
See less
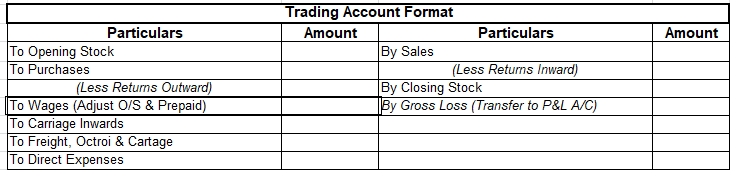
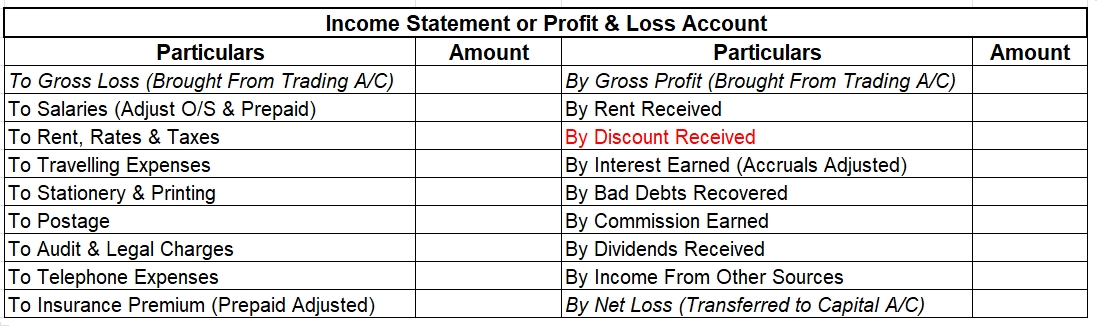
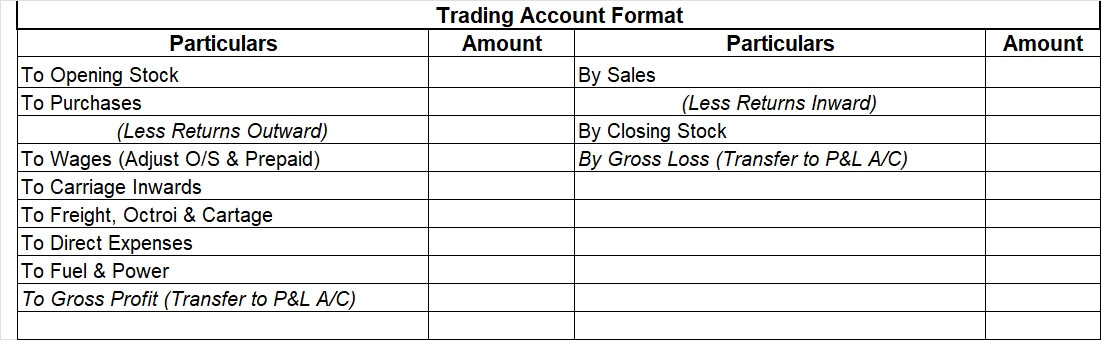
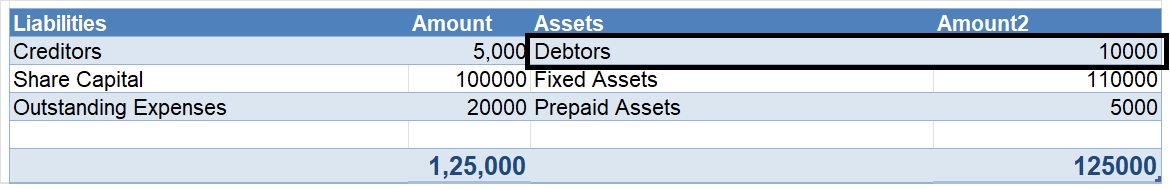
Prepaid expense means a service to be rendered in the future period for which the business has already paid the remuneration. Prepaid expenses are classified as assets. The benefits of this payment will accrue to the business at a later period. For example, insurance is often paid for annually on tRead more
Prepaid expense means a service to be rendered in the future period for which the business has already paid the remuneration. Prepaid expenses are classified as assets. The benefits of this payment will accrue to the business at a later period.
For example, insurance is often paid for annually on the basis of the calendar year. A business may pay insurance every year on 1st January for that entire year. While preparing the financial statements on 31st March, it will recognize the insurance premium for the period 1st April to 31st December of the next financial year as a prepaid insurance expense.
Why are prepaid expenses classified as assets?
First of all, let us understand what an asset is. An asset is anything over which the business has ownership rights and which it can sell for money. The benefits of this asset should accrue to the business.
In light of this definition, let us analyze prepaid expenses as an asset. As the business has already paid for these goods or services, it becomes a legal right of the business to receive the relevant goods or services at a later date. As the benefit of this expense would accrue to the business only at a later date, the prepaid expenses are classified as an asset.
Some examples of prepaid expenses are prepaid insurance, prepaid rent etc
Treatment of Prepaid Expenses
Prepaid expenses are recorded in the balance sheet under the heading “Current Assets” and sub-heading “Other Current Assets”
As per the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles or GAAP, expenses must be recognized in the accounting period to which they relate or in which the benefit due to them is likely to arise. Thus, we cannot recognize the prepaid expenses in the accounting period in which they are incurred.
Prepaid assets are classified as assets and carried forward in the balance sheet to be debited in the income statement of the accounting period to which they relate.
Adjusting Entries
Adjusting entries are those entries that are used to recognize prepaid expenses in the income statement of the period to which they relate. These entries are not used to record new transactions. They ensure compliance with GAAP by recognizing the expenses in the period to which they relate.
Conclusion
The GAAP and basic definition of an asset govern the treatment of prepaid expenses as an asset. The business incurs them in an accounting period different from the accounting period in which their benefit would accrue to the business. The business has a legal right to receive those goods or services.
The business carries them as a current asset on the balance sheet. In the relevant accounting period, they are recognized in the income statement.
See less